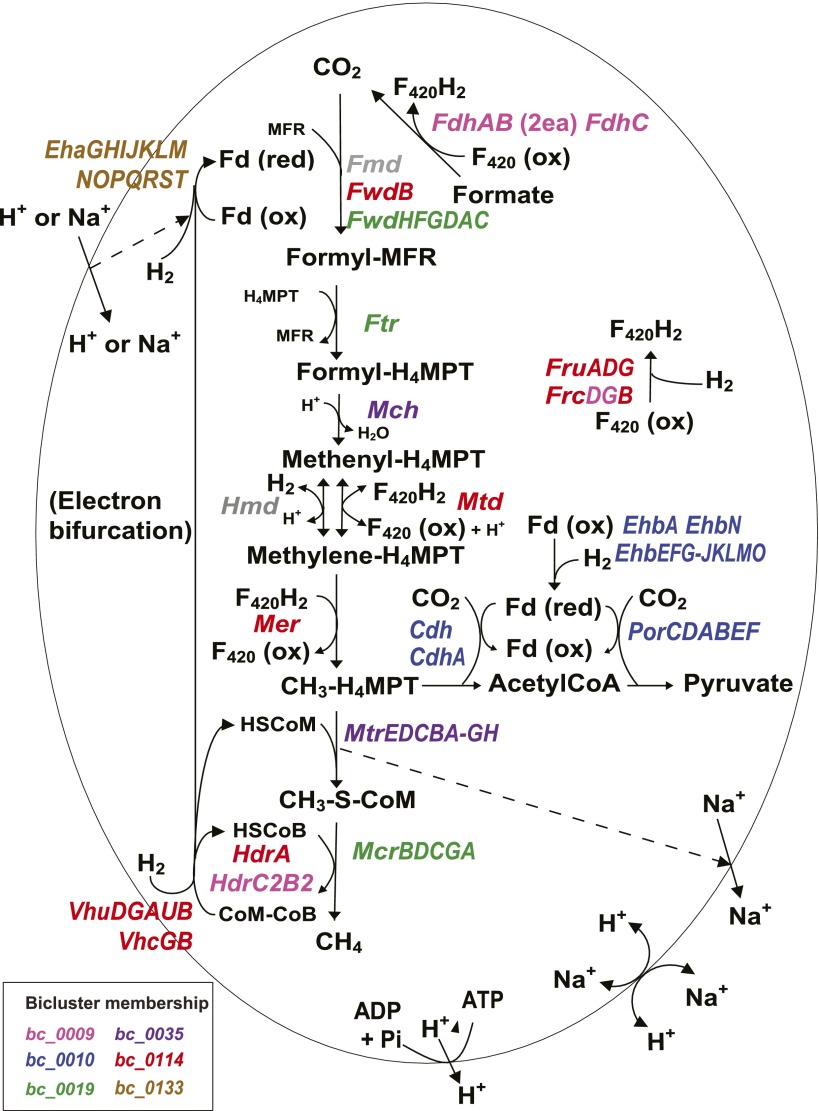
Figure 2.
Differential regulation of methanogenesis genes. Methanogenesis pathway of M. maripaludis together with corresponding bicluster membership information is shown. Methanogenesis from CO2 occurs in four reduction steps, two C-1 transfer steps, and one dehydration step. Note that the Fd that donates electrons to Fmd/Fwd can be reduced in two ways—by electron bifurcation from Hdr or by the Eha hydrogenase. Dotted arrows indicate coupling of metabolic steps with membrane ion gradients. Biosynthetic CO2 fixation to acetylCoA and pyruyvate is also shown. Colors in enzyme designations denote bicluster membership as indicated in the color key in the lower left corner (see Fig. 4 for their member genes). The main methanogenesis pathway genes are included in four biclusters, bc_0114 (red), bc_0009 (pink), bc_0019 (green), and bc_0035 (purple). The other two biclusters, bc_0133 (brown) and bc_0010 (blue), include genes involved in reactions that are related to methanogenesis such as electron bifurcation and carbon fixation (see text for details). Transcriptional changes of member genes of each of the biclusters are shown in Supplemental Figure S2. Genes encoding enzymes: (Cdh) carbon monoxide dehydrogenase/acetylCoA synthase; (Eha) energy-conserving hydrogenase A; (Ehb) energy-conserving hydrogenase B; (Fdh) formate dehydrogenase; (Fmd/Fwd) formyl-methanofuran dehydrogenase; (Fru/c) F420-reducing hydrogenase; (Ftr) formyl-methanofuran-H4-methanopterin formyltransferase; (Hdr) heterodisulfide reductase; (Hmd) H2-dependent methylene-H4-methanopterin dehydrogenase; (Mch) methenyl-H4-methanopterin cyclohydrolase; (Mcr) methyl-coenzyme M reductase; (Mer) methylene-H4-methanopterin reductase; (Mtd) F420-dependent methylene-H4-methanopterin dehydrogenase; (Mtr) methyl-H4-methanopterin-coenzyme M methyltransferase; (Por) pyruvate oxidoreductase; (Vhu/c) F420-nonreducing (Hdr-associated) hydrogenase. Metabolites: (Fd) ferredoxin; (MFR) methanofuran; (H4MPT) tetrahydromethanopterin; (CoM) coenzyme M.