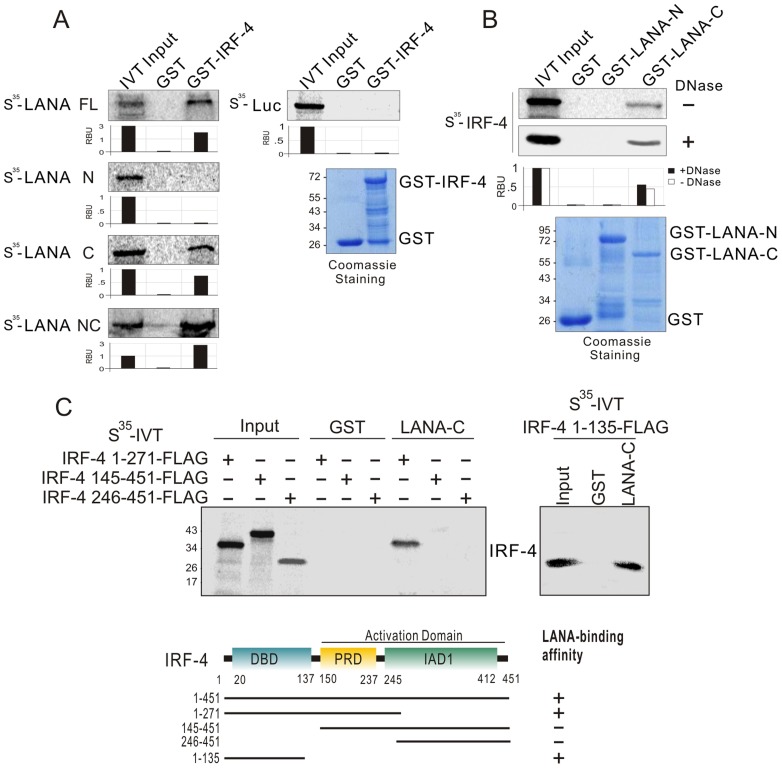
Figure 6. IRF-4 binds with LANA through its DNA-binding domain in vitro.
(A) IRF-4 binds to C-terminal domain of LANA in vitro. The 35S-radiolabeled in vitro-translated proteins of LANA truncated mutants were pre-cleared with GST bead, followed by incubation with GST or GST-IRF-4 beads. The bound protein mixtures were resolved by appropriate SDS-PAGE, and protein species detected by autoradiography. 5% of in vitro translated protein is used as input. The quantification of relative amount of bound proteins (RBU) is shown at the bottom. (B) The 35S-radiolabeled in vitro-translated full length IRF-4 was pulled down by truncated mutants of LANA fusion with GST (GST-LANA N1–340 and C945–1162) in the presence or absence of DNase I (20 U/ml) treatment. Coomassie blue staining of purified GST-LANA is shown at the bottom panels. (C) LANA binds to N-terminal domain of IRF-4 in vitro. The 35S-radiolabeled in vitro-translated proteins IRF-4 with FLAG tag (1–135, 1–271, 145–451 and 246–451) was pulled down by GST or GST-LANA C. Schematics illustrate different structural domains of IRF-4 with LANA-binding ability.