Fig. 4.
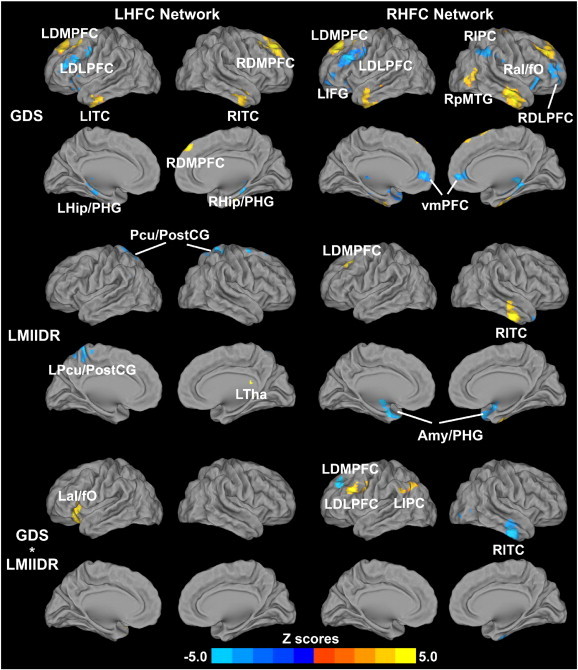
Behavioral significance of the bilateral hippocampal functional connectivity networks across all subjects (p < 0.05, AlphaSim correction). Top row: Main effects of the depressive symptoms on the bilateral HFC networks; Middle row: Main effects of the episodic memory scores (LMIIDR scores) on the bilateral HFC networks. Bright color indicates positive correlation and blue color indicates negative correlation; Bottom row: Interaction of depressive symptoms and memory function on the bilateral HFC networks. Bright color indicates that the interactive effects are positively correlated with bilateral HFC; blue color demonstrates that the interactive effects are negatively correlated with bilateral HFC. Color bar is presented with z scores.
Abbreviations: GDS, geriatric depression scale; LHFC, left hippocampal functional connectivity; RHFC, right hippocampal functional connectivity; LDLPFC, left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; RDLPFC, right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; LDMPFC, left dorsomedial prefrontal cortex; RDMPFC, right dorsomedial prefrontal cortex; LITC, left inferior temporal cortex; RITC, right inferior temporal cortex; LHip/PHG, left hippocampus/parahippocampal gyrus; RHip/PHG, right hippocampus/parahippocampal gyrus; LIPC, left inferior parietal cortex; RIPC, right inferior parietal cortex; LaI/fO, left anterior insula/frontal operculum; RaI/fO, right anterior insula/frontal operculum; LIFG, left inferior frontal gyrus; LTha, left thalamus; L Pcu/PCG, precuneus/postcentral gyrus; Pcu/PCG, precuneus/postcentral gyrus; vmPFC, ventromedial prefrontal cortex; Amy/PHG, amygdala/parahippocampal gyrus; RpMTG, right posterior middle temporal gyrus. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
