Fig. 3.
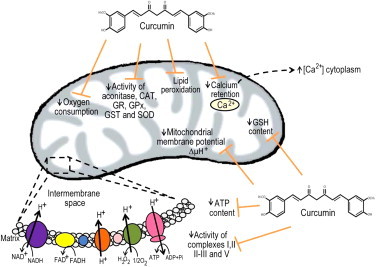
Curcumin is able to prevent mitochondrial dysfunction associated to renal injury. Curcumin is able to prevent lipid peroxidation and the decrease in the following mitochondrial determinations: oxygen consumption, activity of complexes I, II, II-III and V, activity of aconitase and antioxidant enzymes, GSH content, membrane potential, calcium retention and ATP content [51]. GSH (Glutathione), SOD (superoxide dismutase), CAT (catalase), GPx (glutathione peroxidase), GST (glutathione-S-transferase), GR (glutathione reductase), NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, reduced form), FAD+ (flavin adenine dinucleotide), FADH2 (flavin adenine dinucleotide, reduced form), ATP (adenosine triphosphate), ADP (adenosine diphosphate).
