Fig. 1.
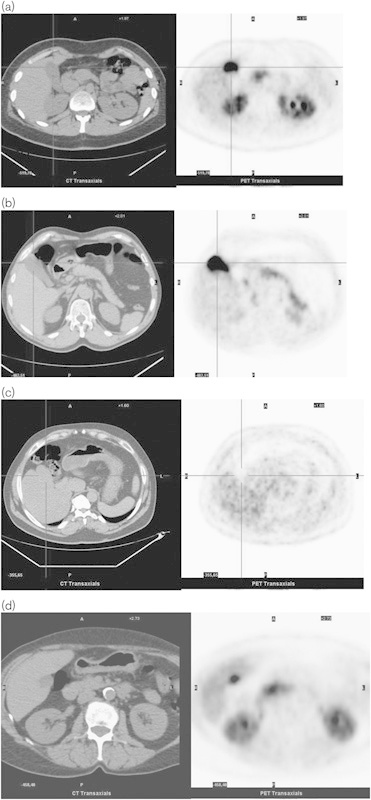
Normal variants of l-6-[18F]fluoro-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (18F-DOPA) uptake in the gallbladder. (a–d) On the left: low-dose computed tomography (CT) transaxial images; on the right: PET images. Images without carbidopa premedication. (a) Intense uptake in the gallbladder. The 18F-DOPA uptake is high in the kidneys as well. Note the focal uptake on the head of the pancreas. (b) Intense uptake in the gallbladder. Note the diffuse 18F-DOPA uptake of the body–tail of the pancreas and the mild uptake of the adrenals, especially the right one. (c) Absent uptake in the gallbladder. (d) Focal intense uptake in the gallbladder that, because of the position, could be misinterpreted as a hepatic lesion. Uptake is high in the kidneys as well. Note the uptake in the head of the pancreas.
