Figure 2.
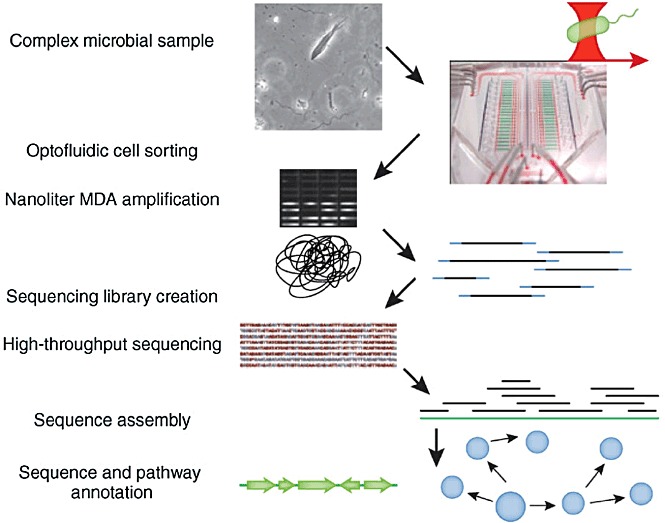
A mixture of cells sampled from a complex microbial ecosystem is introduced into the chip. Single cells are selected using an optical trap, and are sorted into chambers for cell lysis and genome amplification. Genomes are amplified in nanolitre MDA reactions to produce larger quantities of DNA (shown are SYBR Green–stained products in microfluidic reaction chambers). Sequencing libraries are created from the amplified genomic DNA for sequencing on a high‐throughput DNA sequencer. The sequence reads are assembled to recover the genome sequence, which is annotated to identify genes and pathways present in the original cell. Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Nature Methods (Kalisky and Quake, 2011), copyright 2011. The microfluidics image was reprinted from Leslie (2011).
