Figure 1.
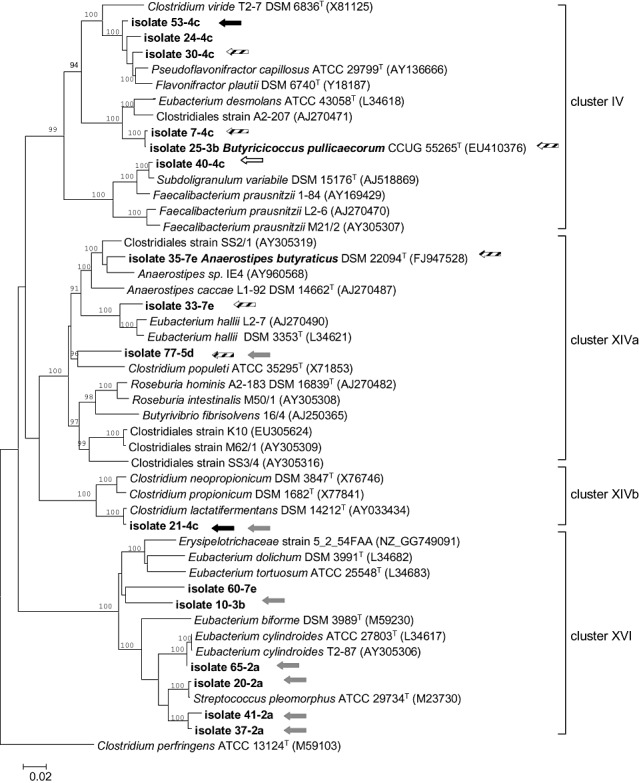
Phylogenetic tree showing the relationship between the different butyrate‐producing chicken isolates based on 16S rRNA gene sequences. The tree was constructed by use of the neighbour‐joining method. The 16S rRNA gene sequence of Clostridium perfringens (ATCC 13124) was used as an outgroup to root the tree. Accession numbers are given in brackets. The numbers shown at the nodes of the tree indicate bootstrap values out of 100 bootstraps resamplings (values under 90% are not shown). The strains isolated in this study are shown in boldface and are labelled with an arrow when possessing a sequence related to the butyryl‐CoA:acetate CoA transferase gene (black arrow: CoATDF1, CoATDR2 primers; striped arrow: CoATDF1, CoATDR2 and BCoATscrF, BCoATscrR primers), the propionate CoA‐transferase gene (grey arrow) or the butyrate kinase gene (white arrow). Scale bar: 0.02 substitutions per nucleotide position.
