Figure 4.
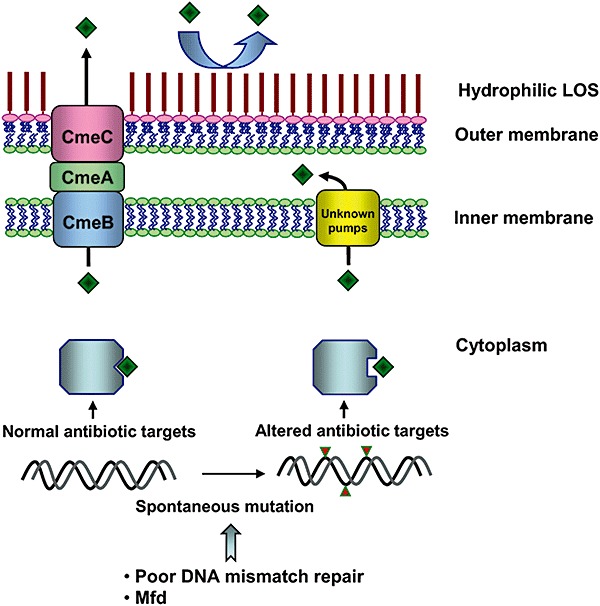
Mechanisms associated with Campylobacter resistance to macrolide and fluoroquinolone antibiotics. LOS reduces the uptake of hydrophobic antibiotics (e.g. macrolide); efflux pumps (such as CmeABC and other uncharacterized efflux transporters) decrease the intracellular concentration of antibiotics; and chromosomal mutations reduce the affinity of antibiotics to their targets. Mfd and the lack of an intact mismatch repair system enhance the spontaneous mutation rate in Campylobacter.
