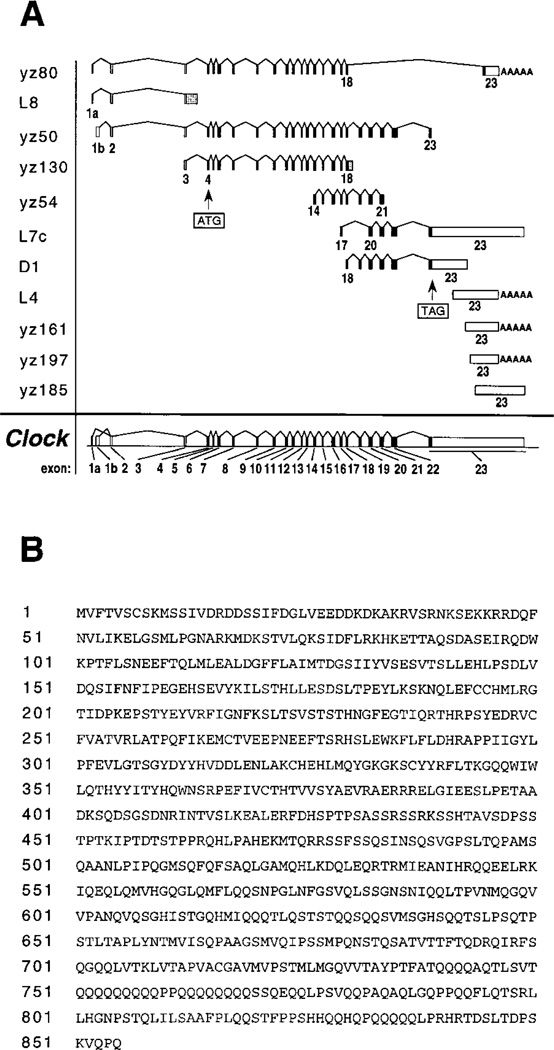
Figure 3. cDNA Clones Identifying the Clock Gene and the Predicted Amino Acid Sequence of the CLOCK Protein.
(A) cDNA clones isolated in the cDNA selection and direct library screening efforts. Clones beginning with yz are derived from cDNA selection, and those beginning with L (LIGHT) or D (DARK) are clones isolated from the direct library screen. Their exon content was determined by alignment to the genomic sequence that was assembled from the M13 shotgun sequencing subclones of BACs 52 and 54. Exon and intron sizes are depicted schematically. Exons 1a–22 vary in size from 71 base pairs (exon 1a) to 295 base pairs (exon 22). Intron sizes vary from 107 base pairs (between exons 10 and 11) to >22 kilobase pairs (between exons 2 and 3). yz80 appears to contain a unique splice variant. L7c appears to be a partial clone of the Clock mutant splice variant transcript. Poly(A) tails of clones yz80, L4, yz161, and yz197 are indicated schematically. Exons containing open reading frames are closed, and exons containing 5′ and 3′ un-translated regions are open. Clones L8 and yz130 were reverse transcribed from intronic poly(A) sequences. The intronic sequences of these clones are shaded. The 2565-base ORF begins at base 44 of exon 4 and ends at base 177 of exon 23. Note the long 3′ un-translated region, which extends for >6 kb.
(B) When translated, the 2565-base ORF predicts a protein of 855 amino acids, dominated by glutamine (112) and serine (100) residues. This protein has an expected molecular mass of 96.4 kDa and a pI of 6.52.