Table 1.
Enaminone Allylic Alkylation Screen.[a]
 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enantiomeric Excess (% ee)[b] | ||||||||
| entry | Substrate | R | Product | ligand | THF | MTBE | Toluene | 2:1 Hex–Tol |
| 1 | 9a | H | 13a | 3 | 87 | 88 | 87 | 87 |
| 2 | 8 | 85 | 86 | 88 | 85 | |||
| 3 | 10a | Oi-Bu | 14a | 3 | 85 | 85 | 86 | 87 |
| 4 | 8 | 86 | 86 | 86 | 88 | |||
| 5 | 12a | NMe(Bn) | 15a | 3 | 61 | 60 | 55 | 52 |
| 6 | 8 | 79 | 78 | 84 | 83 | |||
| 7 | 12b | NPh(Bn) | 15b | 3 | 81 | 87 | 85 | 83 |
| 8 | 8 | 76 | 74 | 82 | 83 | |||
| 9 | 12c | NAc(Bn) | 15c | 3 | 89 | 90 | 88 | 88 |
| 10 | 8 | 83 | 85 | 88 | 86 | |||
| 11 | 12d | NBz(Bn) | 15d | 3 | 86 | 87 | 88 | 87 |
| 12 | 8 | 80 | 83 | 82 | 83 | |||
| 13 | 12e | NBoc(Bn) | 15e | 3 | 87 | 86 | 87 | 82 |
| 14 | 8 | 84 | 84 | 81 | 83 | |||
| 15 | 12f | NTs(Bn) | 15f | 3 | 84 | 83 | 83 | 82 |
| 16 | 8 | 82 | 83 | 83 | 83 | |||
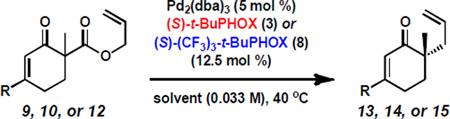
Conditions: enone 9a, vinylogous ester 10a, or enaminone 12a–f (1.0 equiv), Pd2(dba)3 (5 mol %), and (S)-t-BuPHOX (3) or (S)-(CF3)3-t-BuPHOX (8) (12.5 mol %) in solvent (0.033 M) at 40 °C.
Determined by GC, HPLC, or SFC analysis with chiral stationary phase.
Red = with (S)-3 as ligand and blue = with (S)-8 as ligand.
