Figure 6.
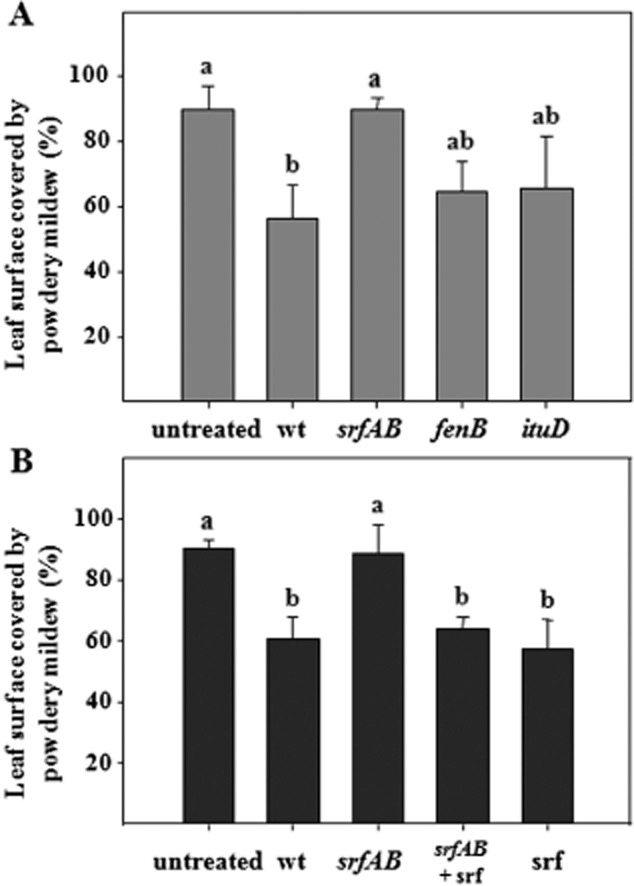
Effect of lipopeptides in the activation of ISR in melon plants against powdery mildew. A. ISR assays using mutants defective in the production of lipopeptides. Melon plants were bacterized with the wild-type strain B. subtilis UMAF6639 and its derivative mutants defective in the production of surfactin, fengycin or iturin A, and inoculated with P. fusca conidia as described in Experimental procedures. B. ISR assays using commercial surfactin. Melon plants were bacterized with wild-type B. subtilis UMAF6639, its surfactin-defective mutant or watered with 10 ml of a solution of 10 μM synthetic surfactin C15. Disease severity expressed as the percentage of leaf surface covered by powdery mildew was recorded 18 days after pathogen challenge. Data represent the means of at least three independent experiments, and bars show the standard deviation. Treatments with the same letter are not significantly different at P = 0.05, according to Fisher's least-significant-difference test. A set of 15–20 plants was tested per treatment. Abbreviations: wt, wild-type B. subtilis UMAF6639; srfAB, surfactin-deficient mutant; fenB, fengycin-defective derivative; ituD, iturin A-deficient transformant; srf, synthetic surfactin.
