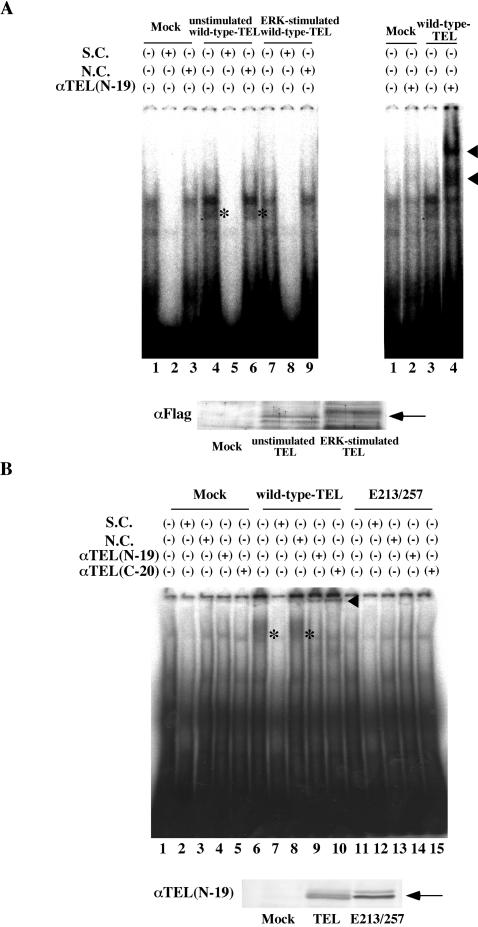
FIG. 6.
(A) Hyperphosphorylated TEL does not bind to DNA. The top left panel shows results of EMSA carried out with the 32P-labeled EBS probe (oligonucleotide A) and mock lysate (lanes 1 to 3), wild-type TEL-expressing COS-7 lysate without activated ERK (lanes 4 to 6), and wild-type TEL-expressing COS-7 lysate with activated ERK (lanes 7 to 9). A 300-fold molar excess of oligonucleotide A (S.C., lanes 2, 5, and 8) or oligonucleotide M (N.C., lanes 3, 6 and 9), which contains mutations in the EBS, was also added to the reaction mixtures. Asterisks indicate a specific DNA-TEL complex-derived band. The top right panel shows results obtained when anti-TEL antibody (lanes 2 and 4) was also added to the reaction mixtures. The supershifted bands are indicated with arrowheads. In the bottom panel, the expression of unstimulated or ERK-stimulated wild-type TEL protein is shown. An arrow indicates overexpressed wild-type TEL proteins. (B) The E213/257 mutant also does not bind to DNA. The top panel shows results obtained when EMSA was carried out with the 32P-labeled EBS probe and mock (lanes 1 to 5), in vitro-translated wild-type TEL (lanes 6 to 10), or E213/257 (lanes 11 to 15) proteins. Asterisks indicate a specific DNA-TEL complex-derived band. A 300-fold molar excess of cold-specific competitor (S.C., lanes 2, 7, and 12) or nonspecific competitor (N.C., lanes 3, 8, and 13) was also added to the reaction mixtures. Two kinds of anti-TEL antibodies (N-19 for lanes 4, 9, and 14 and C-20 for lanes 5, 10, and 15) were added to thereaction mixtures. The supershifted bands are indicated with a solid arrowhead. In the bottom panel, the expression of in vitro-translated wild-type TEL or E213/257 protein is shown. An arrow indicates wild-type TEL or E213/257 mutant proteins.