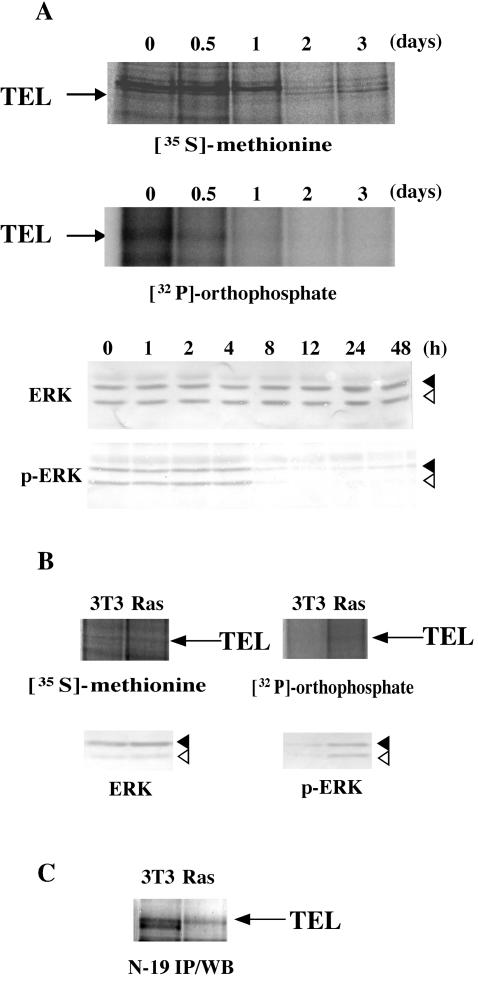
FIG. 8.
(A) Dephosphorylation of endogenous TEL proteins during the course of erythroid differentiation in MEL cells. Parental MEL cells were induced into erythroid differentiation with 5 mM HMBA and subjected to metabolic labeling as described in the legend to Fig. 1C (top panel). Western analyses were performed with anti-ERK or anti-phosphorylated ERK antibody to detect total or phosphorylated ERK proteins (bottom panel). Arrows, solid arrowheads, and open arrowheads indicate endogenous TEL, ERK1, and ERK2 proteins, respectively. (B) Phosphorylation of endogenous TEL proteins through Ras/ERK pathways. Nontransformed or H-Ras-transformed NIH 3T3 clones were subjected to metabolic labeling as described for panel A (top panel). Western analyses were performed with anti-ERK or anti-phosphorylated ERK antibody to detect total or phosphorylated ERK proteins (bottom panel). Arrows, solid arrowheads, and open arrowheads indicate endogenous TEL, ERK1, and ERK2 proteins, respectively. (C) Western analysis with anti-TEL antibody (N-19) for immunoprecipitates with the same antibody from mock or H-Ras-transformed NIH 3T3 cells. An arrow indicates immunoprecipitated TEL.