Figure 1.
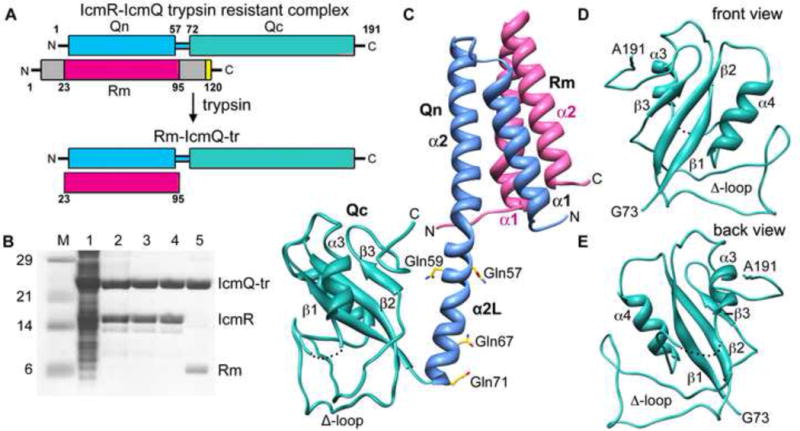
Overview, purification and structure of Rm-IcmQ.
A. A domain diagram for IcmR-IcmQ is shown. Trypsin treatment removes flexible N- and C-terminal regions of IcmR that may be unstructured, and yields the trypsin resistant (tr) Rm-IcmQ complex.
B. The purification of Rm-IcmQ-tr is shown on SDS-PAGE. Molecular weight markers (Lane M), high speed lysate (Lane 1), eluate from HisTrap HP (Lane 2), flow-through from HiTrap Q (Lane 3), eluate from HiTrap Sp (Lane 4), and Rm-IcmQ after trypsinization and purification (Lane 5) are shown.
C. A molecular model of Rm-IcmQ is shown. The middle region of IcmR (Rm, pink) interacts with the N-terminal domain of IcmQ (Qn, light blue) to form the Rm-Qn interacting domain, comprised of a 4-helix bundle. A linker helix (α2L) separates Rm-Qn from the C-terminal domain of IcmQ (Qc, green). Secondary structures are labeled, including the Δ-loop, and four residues mutated to glutamines (aa57, 59, 67 and 71) are also shown.
D. and E. Front and back views are shown of Qc.
See also Figures S1, S2 and S3.
