Figure 5.
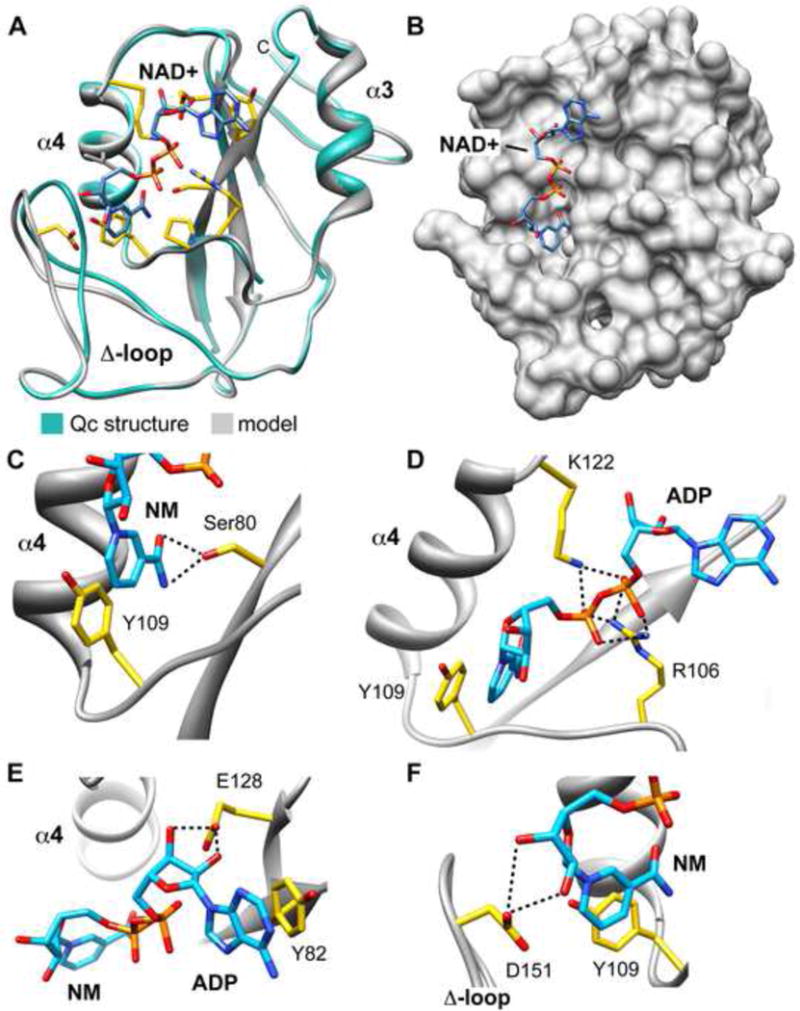
A model of NAD+ bound to Qc.
A. The structure of unliganded Qc (green) is super-imposed with the computational model of NAD+ bound to Qc (grey). Note movement of the Δ-loop and the extended conformation of NAD+ within the scorpion motif. In addition, the modeling restored connectivity of the α3–α4 loop.
B. Modeled NAD+ is shown in an extended conformation bound to a surface groove on Qc.
C. Possible molecular interactions between NAD+ and Qc are shown in panels C–F. Hydrogen bonds are depicted as black dashed lines. Hydrogen bonding interactions between Ser80 and nicotinamide in a small pocket are shown. In addition, a ring stacking interaction between nicotinamide and Tyr109 is present.
D. Hydrogen bonding between the phosphates of NAD+ and Arg106/Lys122 is shown.
E. Ring stacking between the adenine of NAD+ and Tyr82 is present, along with hydrogen bonding between the ribose moiety of ADP and Glu128.
F. Hydrogen bonding is present between Asp151 and hydroxyl groups of the ribose ring attached to the nicotinamide ring.
See also Figure S5.
