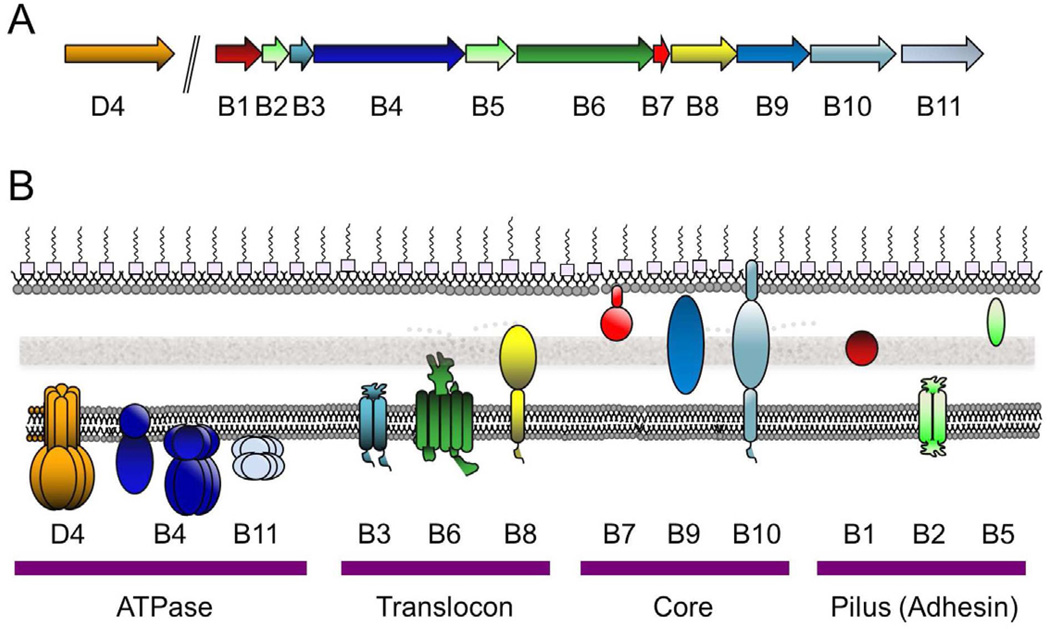
Fig. 1.
The A. tumefaciens VirB/VirD4 T4SS gene organization and subunit subcellular locations. (A) virD4 is co-transcribed with the virD1 relaxase and virD2 accessory factor genes from the virD promoter and the eleven virB genes are transcribed from the virB promoter. (B) VirD4 and VirB proteins are associated with the cytoplasmic membrane (CM), cell-wall (CW) containing periplasm, or outer membrane (OM) as shown. General membrane topologies are denoted as are the oligomeric structures of the VirD4 (hexamer), VirB4 (monomer or hexamer, see text), VirB11 (hexamer) ATPases. VirB7 is an outer-membrane-associated lipoprotein and VirB10 spans both membrane with N- and C-proximal α-helical domains. The VirD4 and VirB subunits are clustered into four functional groups.