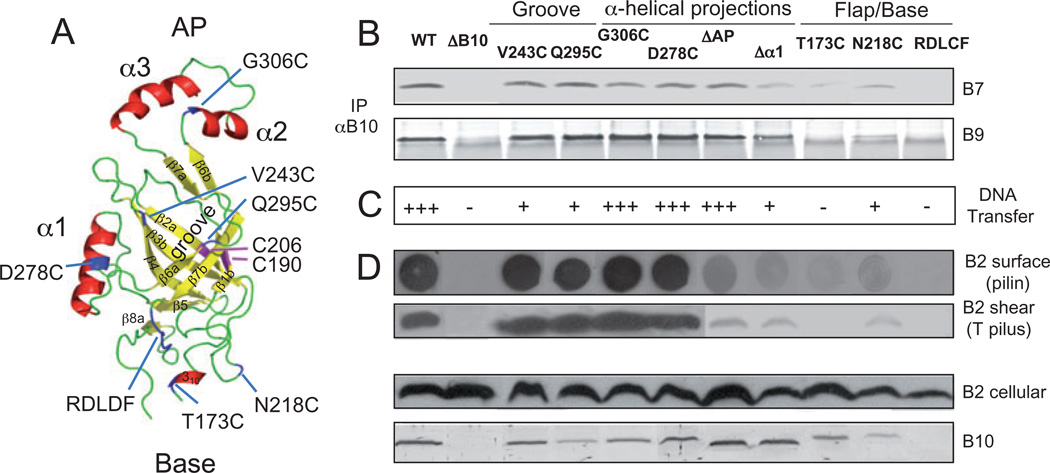
Fig. 5. Modelled β-barrel structure and phenotypes of substitution mutations.
A. A. tumefaciens VirB10 β-barrel ribbon structure modelled with co-ordinates from the H. pylori ComB10 X-ray structure using the Modeller package (Marti-Renom et al., 2000) and PyMOL (http://pymol.org/) to construct the figure. This C-terminal domain (residues 173–377) presents as a non-canonical β-barrel with a groove marked by the V243C and Q295C substitution mutations, a flexible base marked by the S173C and N218C mutations and a conserved RDLDF motif, and two helical projections, α1 marked by D278C and the α2,α3 antennae projection (AP) marked by G306C. Native Cys-190 and Cys-206 residues forming an intramolecular disulphide cross-link are shown in pink; Cys substitution mutations are in blue. β-Strands β1-β7 are identified.
B. Effects of mutations on VirB10 interaction with the outer membrane channel subunits. Material immunoprecipitated from detergent-solubilized cell extracts with anti-VirB10 antibodies (IP αB10) was analysed for co-precipitation of VirB7 and VirB9 by immunoblot development with corresponding antibodies. Experiments were carried out under non-reducing conditions for co-precipitation of the VirB7–VirB9 dimer complex.
C. Effects of mutations on T-DNA transfer as monitored by virulence on wounded Kalanchoe leaves (− avirulent, +++ WT virulence); results correlated with frequencies of IncQ plasmid transfer to agrobacterial recipients (data not shown).
D. Effects of mutations on T pilus production. Extracellular pilin and T pilus, and total cellular pilin and VirB10 derivatives were detected as described in Fig. 2 legend.
Strains: WT, wild-type A348; ΔB10, non-polar virB10 strain PC1010; isogenic PC1010 producing Cys substitution mutants as listed.