Figure 6.
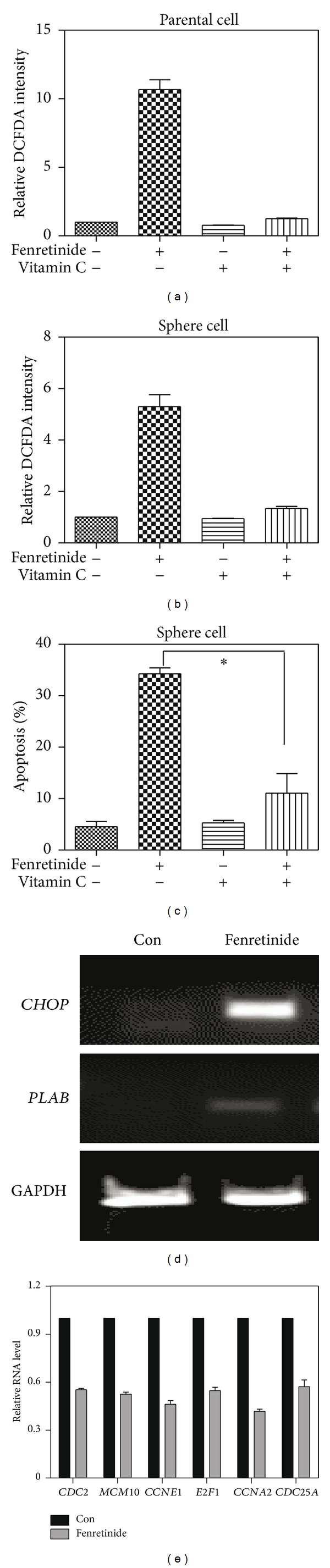
Fenretinide induced ROS induction, ER stress, and cell cycle progression arrest in A2780 cells. (a) Data summary and analysis of DCFDA intensity in A2780 parental cells. DCFDA intensity was detected after 3 μM fenretinide or 100 μM vitamin C or combined fenretinide and vitamin C treatment for 3 hrs in A2780 parental cells. The untreated parental cells were used as normalization control. Means and standard errors of relative ROS level from three experiments were shown. (b) Data summary and analysis of DCFDA intensity in A2780 sphere cells. DCFDA intensity was detected after fenretinide or vitamin C or combined fenretinide and vitamin C treatment for 3 hrs in A2780 enriched sphere cells. (c) Data summary and analysis of apoptosis in A2780 enriched sphere cells. Apoptotic cells were detected through AnnexinV/PI assay, after fenretinide or vitamin C or combined fenretinide and vitamin C treatment for 24 hrs in A2780 enriched sphere cells. Means and standard errors of apoptosis percentages from three experiments were shown. ∗, statistically significant difference between A2780 enriched sphere cells treated with fenretinide combined vitamin C treatment and fenretinide treatment group (P = 0.0278). (d) mRNA expression of CHOP and PLAB genes in A2780 sphere cells. A2780 sphere cells were treated with 3 μM fenretinide for 6 hrs. mRNA expression of CHOP and PLAB genes were detected by PCR. Products were separated by electrophoresis, GAPDH as a housekeeping gene for loading control. (e) Data summary and analysis of mRNA expression in A2780 sphere cells. mRNA expression of CDC2, MCM10, CCNE1, E2F1, CCNA2, and CDC25A was detected by real-time RT-PCR. The results were obtained from three independent experiments.
