Table 4. Sequence diversity and distribution of naturally occurring vasopressin-like nonapeptides.
| Peptide | Sequence‡ | Organism(s) | Ref.§ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vasopressin | CYFQNCPRG* | Eutherian mammals | P01185 |
| Lysopressin | CYFQNCPKG* | Marsupials and pigs | P01183 |
| Phenypressin | CFFQNCPRG* | Marsupials | 0909223B¶ |
| Vasotocin |
CFITNCPPG* CFVRNCPPG* CFISDCARG* |
Daphnia pulex
Platynereis dumerilii Saccoglossus kowalevskii |
E9H8T6 A6YIC5 D1LXH6 |
| Ile4-vasotocin | CYIINCPRG* |
Branchiostoma
floridae |
[23] |
| Conopressin# | CFIRNCPP* | Conus textile | P86255 |
| γ-conopressin vil# | CLIQDCPEG* | Conus villepinii | P85141 |
| [Arg]-conopressin S# | CIIRNCPRG* | Conus striatus | P05487 |
| [Lys]-conopressin G | CFIRNCPKG* | Leeches and molluscs | P05486 |
| Conopressin T# | CYIQNCLRV* | Conus tulipa | [15] |
| Inotocin |
CLITNCPRG* CLIVNCPRG* |
Arthropods, ants Camponotus floridanus |
A3RE83 [2] |
| Vasotocin (ancestral)†† | CYIQNCPRG* | Nonmammalian vertebrates |
P69129 |
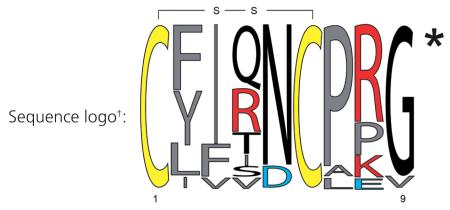
Relative frequency sequence logo plot, conserved cysteine residues are highlighted in yellow, hydrophobic, aromatic and non-polar amino acids are labeled in gray, negatively charged residues are labeled in blue and positively charged residues are labeled in red. All sequences are amidated at the C-terminus, as indicated by the asterisk.
Conserved cysteine residues forming a disulfide bond are highlighted in bold. All sequences are amidated at the C-terminus, as indicated by the asterisk.
UniProtKB entry, unless otherwise stated.
GenBank protein accession number.
Peptides from Conus spp. have been isolated from venom ducts, glutamic acid represents γ-carboxyglutamate.
Presumed ancestral oxytocin/vasopressin nonapeptide [2].
