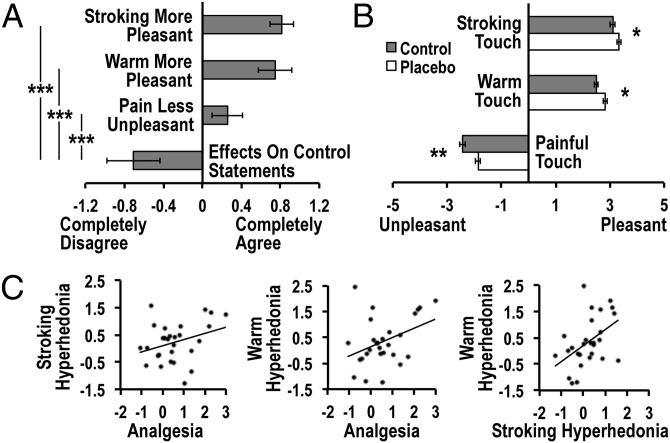
Fig. 1.
Behavioral results. (A) After watching the documentary, participants indicated a positive expectation that intranasal oxytocin treatment would induce stroking touch and warm touch hyperhedonia, as well as analgesia, but no expectation of oxytocin effects on irrelevant control statements. (B) Compared with the control condition, placebo treatment increased pleasantness of stroking and warm touch, and decreased unpleasantness of painful touch. (C) The magnitude of placebo responses [defined as the (placebo > control) difference in VAS scores] correlated across stimulus types. Error bars represent SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.