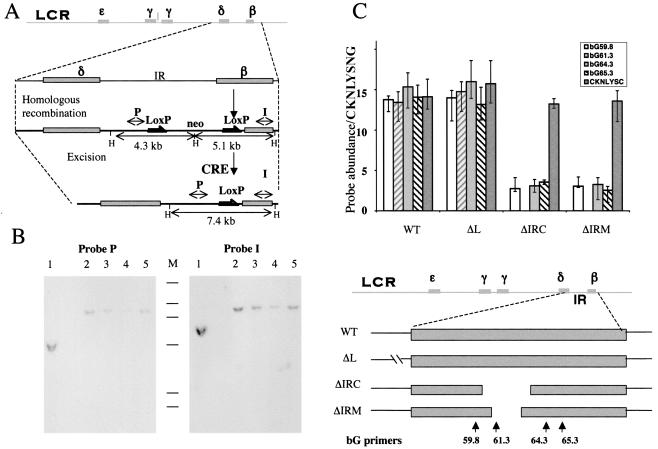
FIG. 7.
Requirements for replicator activity within the human β-globin locus in the context of an intact human chromosome 11. The entire human chromosome 11 was transferred to the chicken DT40 cell line, as described previously (16). The indicated regions were deleted from the human β-globin locus: ΔIRC, deletion of a 1.7-kb fragment between the PmeI and MfeI sites; ΔIRM, deletion of a 500-bp fragment between the SnaBI and BspMI sites; and ΔL, deletion of a fragment between two PmlI sites 5′ of the IR. (A) Illustration of the homologous recombination followed by CRE-mediated excision of the IR fragments (for details, see reference 16). The top line shows a schematic illustration of the entire β-globin locus; the β-like globin genes are shown as shaded boxes. The second line shows a magnification of the IR region between the δ and the β genes. The third line shows the structure of a recombinant in which a neomycin resistance gene (neo) flanked by LoxP sites (grey arrows) replaced a part of the IR by homologous recombination. The fourth line shows the structure of a chromosome created by Cre-mediated excision, which deleted a part of the IR, leaving a LoxP site. Double-headed arrows designated P or I represent the location of probes from the human β-globin locus that straddle the inserted LoxP sites. These probes were used in the hybridization experiments shown in panel B. Sites marked by the letter H represent HindIII restriction sites. (B) Southern blot analysis of the structure of ΔIRC. Genomic DNA (10 μg) was digested with HindIII, fractionated on a 0.6% agarose gel, immobilized on a nylon membrane, and hybridized with probes designated I and P as indicated. Lanes 1 contain DNA from a homologous recombinant (third line from the top in panel A); lanes 2 to 5 contain DNA from three different clones resulting from CRE-mediated deletion. Lane 3 contains DNA from the chosen clone ΔIRC. M, molecular size markers derived from 32P-labeled HindIII digestion of bacteriophage λ DNA ranging from 2.3 to 23 kb. The insertion of the neo marker into the globin locus introduced a HindIII site. The two probes, P and I, identified two separate HindIII fragments in the homologous recombinant (4.3 kb and 5.1 kb). After excision, one of the HindIII sites was eliminated and both probes identified a 7.4-kb fragment. Excision was also verified by lack of hybridization to a probe containing the neomycin gene (data not shown). (C) Initiation of DNA replication was measured by the nascent-strand abundance assay as described in the legends to Fig. 1 and 2, using primers from the human β-globin locus except for the CKNLYSC and the CKNLYSNG primers, which were derived from the chicken lysozyme locus (see Table 1 for sequence information). The primer pair CKNLYSNG, which is not abundant in nascent strands from chicken cells (45), served as a standard. Primer locations are illustrated below the histograms. The ΔIRC and ΔIRM chromosomes did not initiate DNA replication, whereas the unaltered chromosomes and the ΔL chromosomes initiated DNA replication from the IR. WT, wild type.