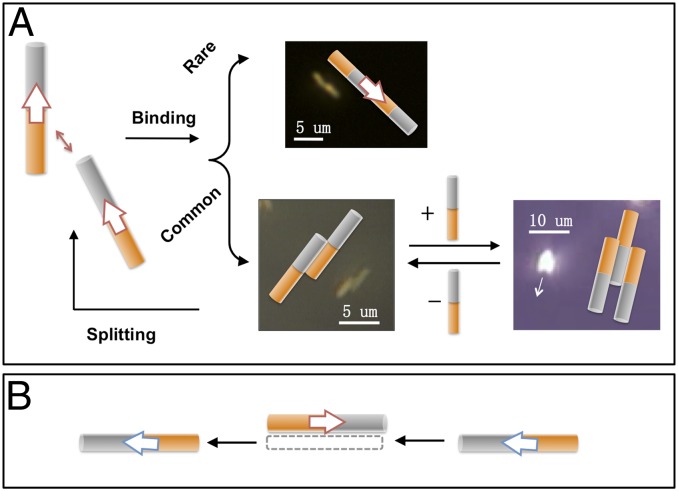
Fig. 1.
Interactions between self-electrophoretic nanomotors moving in the same and opposite directions. (A) Two nanomotors moving in the same direction can form a staggered doublet that moves in a clockwise or counterclockwise arc. Such doublets can attract a third nanomotor to form triplets. In rare cases two nanomotors can associate with each other head-to-tail. (B) The interaction between two nanomotors moving in the opposite direction is typically much more short-lived and weaker.