Figure 4. Cross-dataset and cross-species comparisons reveals evolutionary conserved genome-wide chromosome organization.
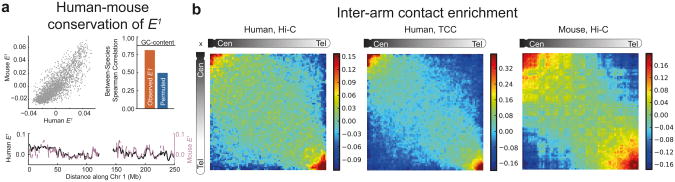
(a) (top left) Scatter plot of E1 for human vs. mouse in syntenic regions; (top right) comparison of observed between-species correlation of E1 (r =.81, P < 1e-10) with GC-content stratified permuted data (r =.50, P < 1e-10); (bottom) human vs. syntenic mouse E1 along human chr1; gaps in the mouse profile reflect regions of human chr1 without a corresponding syntenic region in mouse. Human E1 is for TCC HindIII10 data, mouse E1 was calculated for mouse Hi-C16 data. (b) Heatmaps of iteratively-corrected inter-chromosomal contact probability averaged over all chromosomal arm pairs; heatmaps show the natural log of the contact enrichment, re-scaled and re-binned to 80×80 map (see Online Methods). The data are for human lymphoblastoid Hi-C HindIII8, human lymphoblastoid TCC10, and mouse pro-B cell Hi-C16. 16
