Figure 2. The effects of SNL and PBN treatment on paw withdrawal responses and EGFP+ GABA neuron numbers.
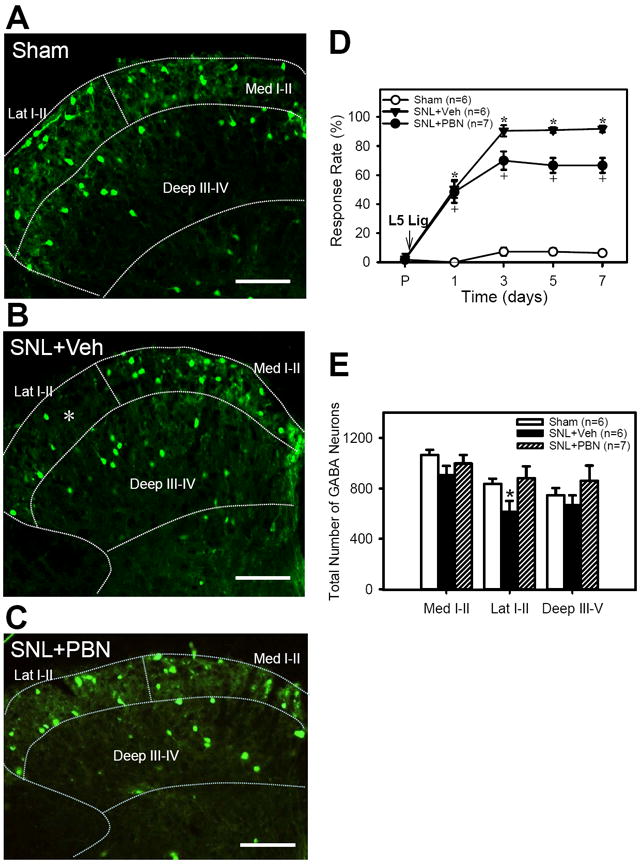
A - C: examples of micrographs of EGFP+ GABA neurons in the ipsilateral L5 spinal dorsal horn one week after sham (A) and SNL surgery with daily vehicle injections of vehicle(B) or PBN (C). The boundaries of medial and lateral laminae I-II (Med I-II and Lat I-II) and deep laminae (Deep III-IV) are outlined with dotted lines. Note that the appearance of EGFP+ GABA neurons were decreased in the lateral half of the superficial dorsal horn after SNL+Veh (indicated by white *) but recovered after SNL+PBN. Scale bar = 100 μm. D: Foot withdrawal response rates to vF stimuli immediately before (P) and on 1, 3, 5 and 7 days after surgery in Sham, SNL+Vehicle, and SNL+PBN mice (tests done just before the first injection of drug on a day). SNL significantly increased the response rates, thus indicating the development of mechanical hyperalgesia. Repetitive PBN treatment (SNL+PBN) partially reduced response rates when compared to vehicle treatment (SNL+Veh). E: The number of EGFP+ GABA neurons for the medial (Med I-II) and lateral halves (Lat I-II) of superficial laminae (I-II) and the deep laminae (Deep III-V) of ipsilateral L5 cord. The EFGP+ GABA neuron numbers were significantly decreased only in the Lat I-II on the ipsilateral side as compared to that of sham. Repetitive PBN treatment (SNL+PBN) reversed the SNL-induced EGFP+ GABA neuron decrease in the Lat I-II. Data are presented as means ± SEM. *, the value is significantly (p < 0.05) different from the sham by ANOVA followed by the Holm-Sidak post-hoc test.
