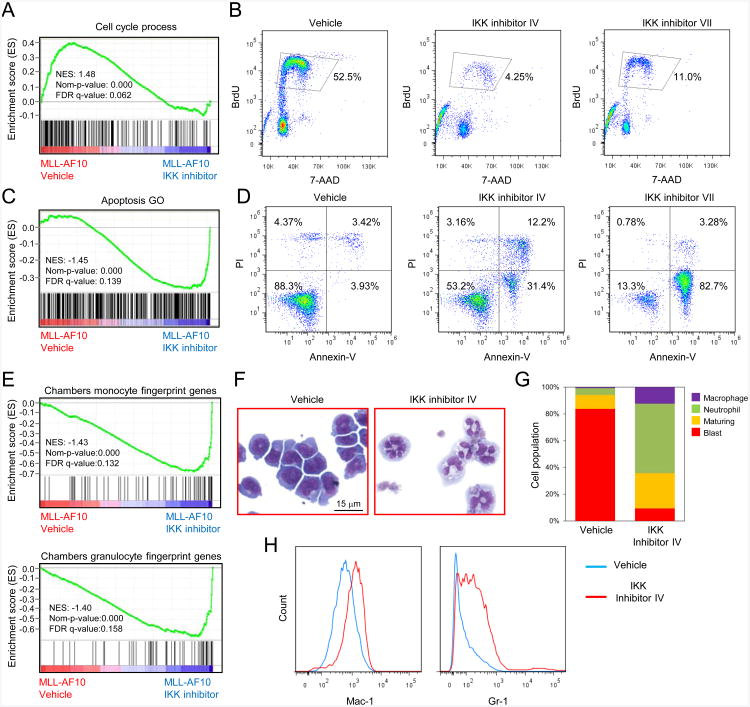
Figure 5. IKK inhibition decreases proliferation, increases apoptosis and induces differentiation of MLL leukemia cells.
(A) GSEA plot shows downregulation of cell cycle process related genes in mouse MLL-AF10 leukemia cells treated for 24 hr with IKK inhibitor versus vehicle treated cells.
(B) Mouse MLL-AF10 leukemia cells were cultured in the presence of 2 μM IKK inhibitor IV or 0.5 μM IKK inhibitor VII for 2 days, and BrdU incorporation was quantified by flow cytometry analysis.
(C) GSEA plot shows upregulation of apoptosis related genes in mouse MLL-AF10leukemia cells treated for 24 hr with IKK inhibitor versus vehicle treated cells.
(D) Mouse MLL-AF10 leukemia cells were cultured in the presence of 1 μM IKK inhibitor IV or 0.5 μM IKK inhibitor VII for 3 days. The annexin-V positive and PI negative populations constitute early apoptotic cells.
(E) GSEA plots show upregulation of monocyte or granulocyte fingerprint genes in mouse MLL-AF10 leukemia cells treated for 24 hr with IKK inhibitor versus vehicle treated cells.
(F) Light microscopy of May-Grunwald/Giemsa-stained mouse MLL-AF10 leukemia cells after 2 days of IKK inhibitor IV treatment (2 μM).
(G) Quantification of leukemia cell populations with indicated morphological features after 2 days of IKK inhibitor IV treatment (2 μM).
(H) Flow cytometry analysis of Mac-1 and Gr-1 surface expression by mouse MLL-AF10 leukemia cells after 2 days of 2 μM IKK inhibitor IV treatment.
See also Figure S5 and Table S3.