FIG. 1.
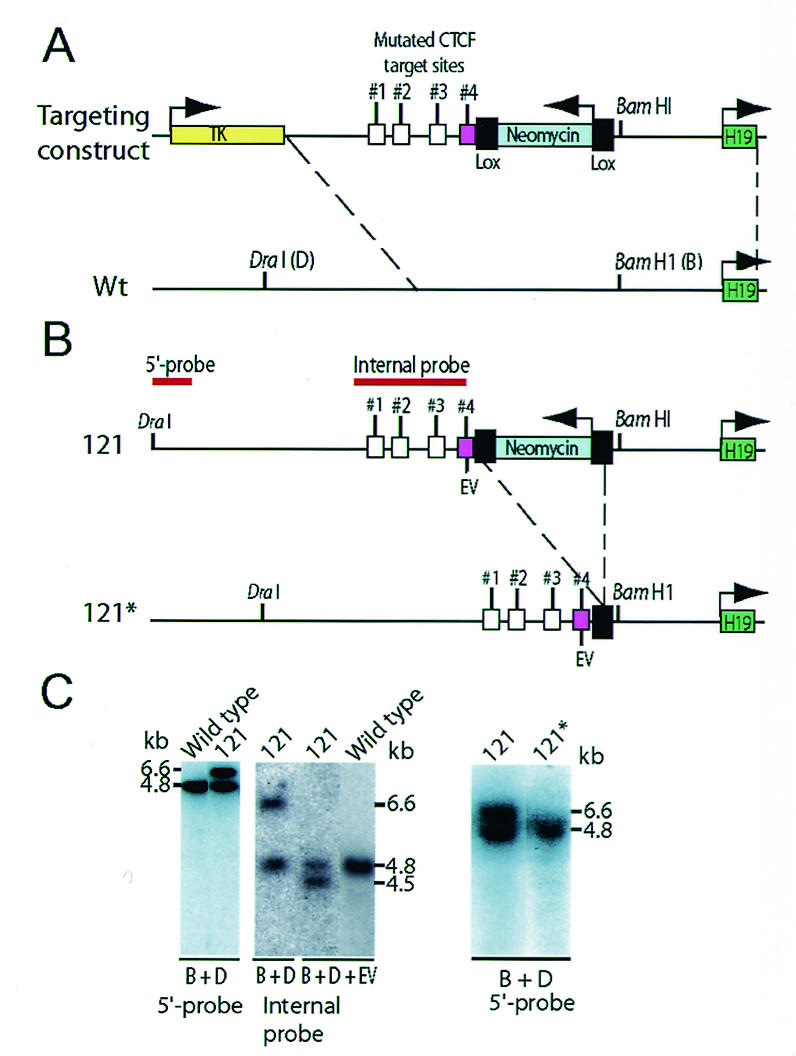
Schematic illustration of the knock-in strategy. (A) Recombination map of the targeting construct and endogenous H19 ICR. CTCF target site 4 (cerise box) was targeted in the knock-in procedure. Wt, wild-type. (B) Deletion of the neomycin gene by breeding mice of strain 121 with mice harboring a β-actin promoter-driven Cre recombinase gene to generate the 121* substrain. (C) The recombination event in clone 121 was assessed by using a probe that is positioned 5′ of the sequence covered in the targeting construct. The properly recombined insert generated a larger fragment due to the extra sequence information provided by the neomycin gene. The mutated targeting allele replaced the endogenous sequence in clone 121 as confirmed by EcoRV (EV) digestion and Southern blot analysis. The mutated allele of the 121* strain is indistinguishable from the wild-type allele when digested with BamHI (B) and DraI (D). For additional information, see the text.
