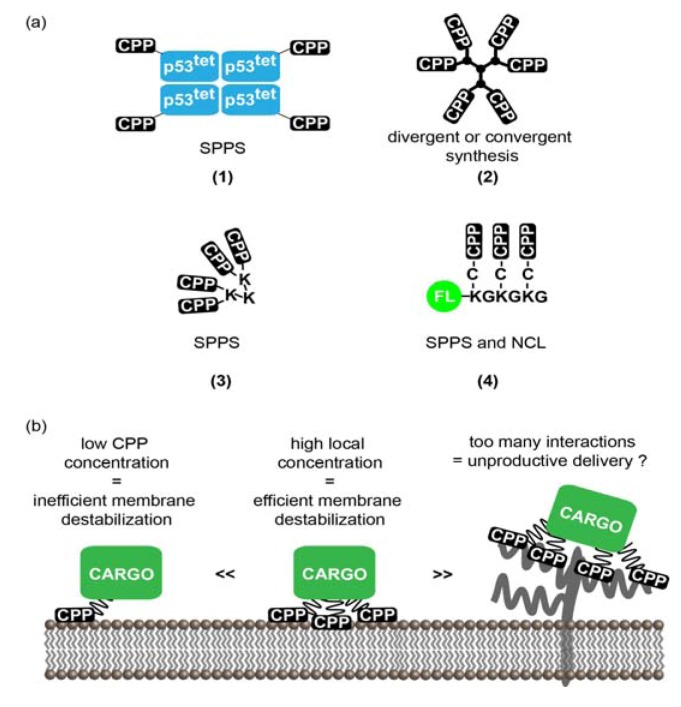
Figure 2.
MCPPs systems and their interactions with membranes. (a) Strategies used to generate MCPPs. From left to right: (1) The p53tet-CPP system involves connecting the tetramerization domain from the human tumor repressor protein p53 to a CPP. The peptide sequence is generated using SPPS. After purification of the peptide sequence, p53tet self-assembles into a tetramer producing a tetravalent CPP. (2) Loligomers are a “squid-like” MCPP system. The CPP is attached on the surface of a polylysine branch scaffold. The scaffold and the peptide are generated using SPPS. The number of branches of this MCPP system will depend on the number of Lys coupling steps. (3) The branched CPP system involves the generation of a peptide scaffold of Lys(ε-NH-Cys)Gly repeats to which a CPP-thioester is added using native chemical ligation (NCL). The peptides were generated using SPPS although production of recombinant peptide or protein thioesters is possible using intein fusions [100,101]. A fluorophore was added on the N-terminal end of the scaffold peptide to serve as both an imaging agent and a small model cargo. (4) Dendrimers are MCPPs having a “tree-like” shape and are usually generated using divergent or convergent methods. CPPs have been attached to the surface of polyamidoamine (PAMAM), polypropylenimine (PPI) or polyethylenimine (PEI) dendrimers. The number of CPPs on dendrimers is among the highest observed for MCPPs. (b) Possible model of mode of action of CPPs versus that of MCPPs. In this example, a CPP-cargo is present at the membrane of endosomes at a low local concentration, leading to poor endosomolytic activity. In contrast, a MCPP-cargo displays multiple copies of the CPP. This leads to efficient membrane interactions and a possible enhancement in membrane disruption. In some cases however, too many CPP copies might cause unproductive membrane interactions such as tight binding to HSPGs. This in turn might lead to poor cellular penetration.