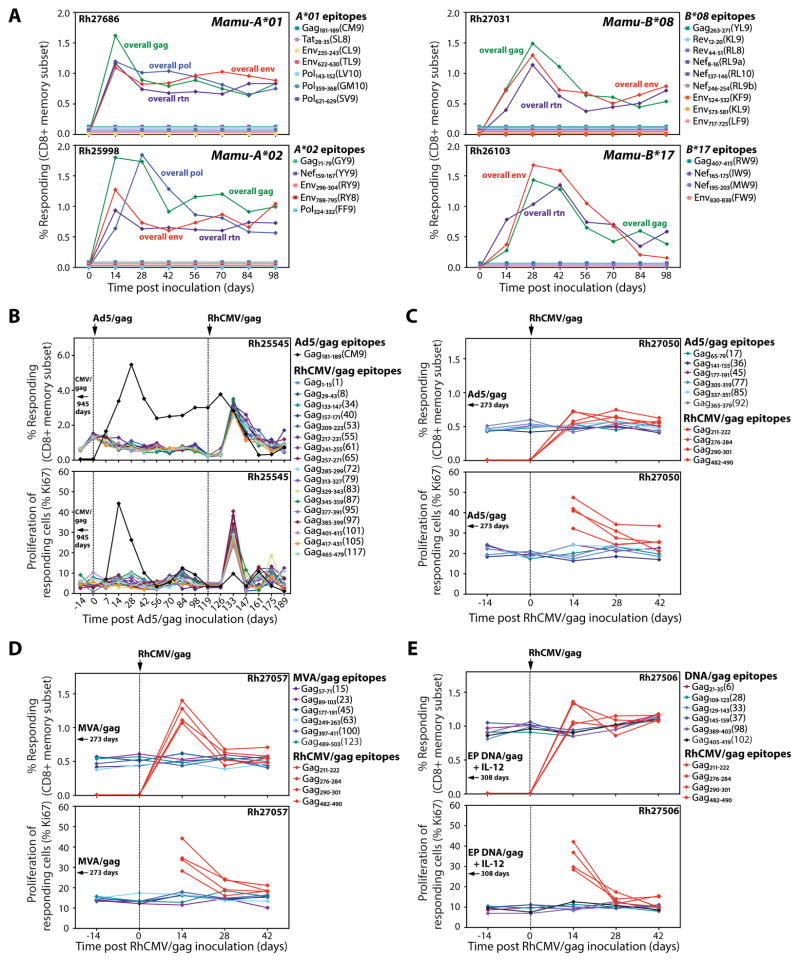
Fig. 1.
Lack of epitope overlap between RhCMV vector-elicited and conventional SIV-specific CD8+ T cell responses. (A) Flow cytometric ICS was used to follow the development of overall SIV insert- and canonical epitope-specific CD8+ T cell responses (responder = TNF-α + and/or IFN-γ +) in the blood of 4 RM, each with a different well characterized MHC-I allele (Mamu-A*01, -A*02, -B*08 and -B*17), after vaccination with strain 68-1 RhCMV/SIVgag, rev/tat/nef (rtn), env, and pol vectors. No response above background was observed for any canonical epitope. (B) The CD8+ T cell response to individual SIVgag 15mer peptides and the canonical Gag181-189 (CM9) epitope was determined in a long-term strain 68-1 RhCMV/gag-vaccinated, Mamu-A*01+ RM (Rh25545) using flow cytometric ICS. The frequency of these responses in blood and the proliferative status of the responding cells (as measured by Ki-67 expression on TNF-α + and/or IFN-γ + events) were followed after boosting with Ad5/gag, and then 119 days later, after re-vaccination with strain 68-1 RhCMV/gag. Gag181-189 (CM9)-specific responses were not detected prior to administration of Ad5/gag. (C–E) The CD8+ T cell response to individual SIVgag 15mer peptides was determined in RM vaccinated with Ad5/gag (C, Rh27050), MVA/gag (D, Rh27057), and electroporated DNA/gag + IL-12 (E, Rh27506), and these responses were followed after vaccination with strain 68-1 RhCMV/gag as described in B. These figures also show induction of 4 SIVgag 15mer-specific CD8+ T cell responses after RhCMV/gag vaccination that were not detectable in the pre-existing SIVgag-specific responses elicited by the conventional vaccines.