Figure 1. M. tuberculosis increases mAIM serum levels in an in vivo infection model.
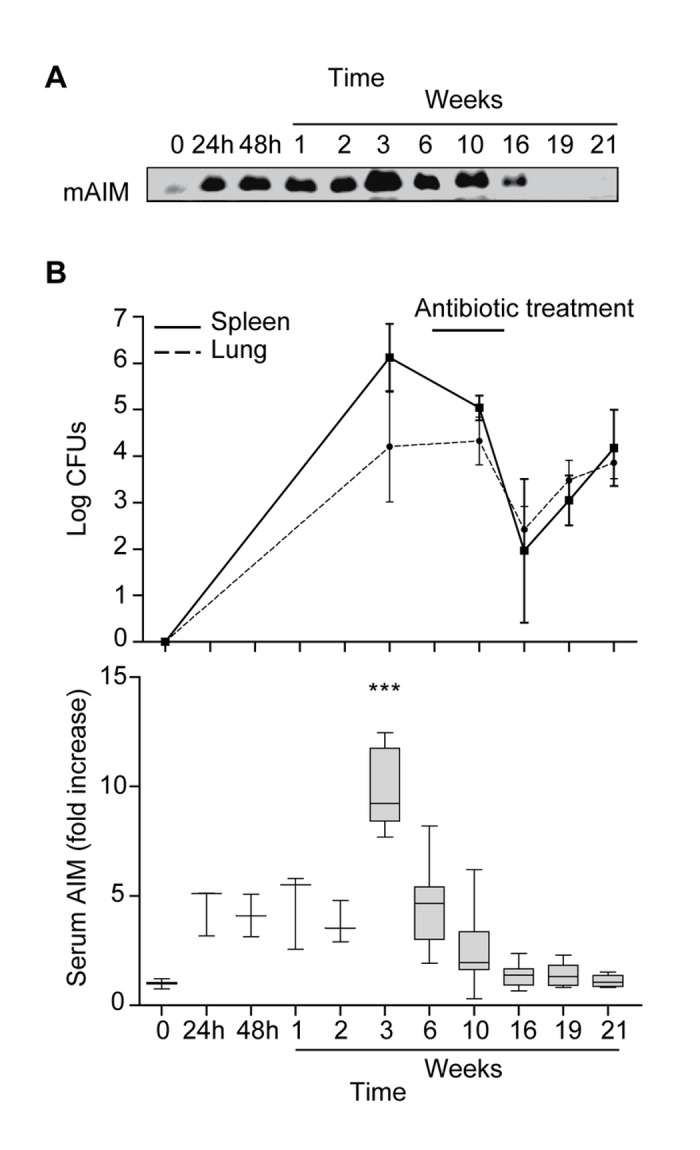
C57BL/6 mice were infected with M. tuberculosis H37Rv through aerosol inoculation. Mice were treated with INH/RIF for 8 weeks (w6 to w14) at which point antibiotic was withdrawn, and infection was allowed to reactivate. mAIM serum levels and bacillary load in the lung and spleen were measured at several time points post-infection (24 h - 21 weeks). A) Representative image of mAIM levels analyzed by Western blot of serum samples. B) Graphs showing spleen and lung bacterial loads at the indicated times (upper graph) and mAIM protein intensity (lower graph) data. Box plots show median values and 5-95 percentile values, from 1µl serum (n=3 to n=5). Fold induction levels were calculated using as reference the serum mAIM from a pool of 5 C57BL/6 uninfected healthy animals, set as 1. *p≤0.05; **p≤0.01; ***p≤0.001 two-way ANOVA.
