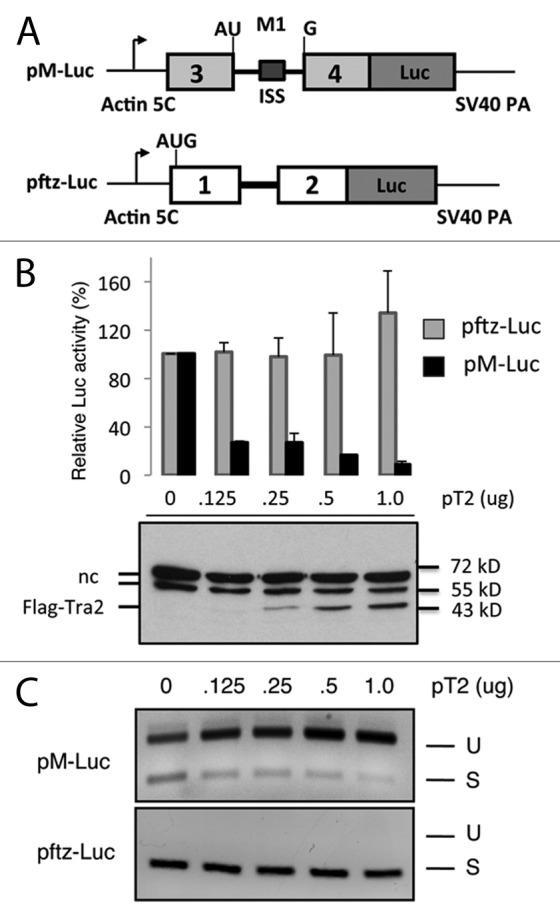
Figure 1. A luciferase reporter detects specific repression of M1 splicing. (A) The organization of reporter plasmids used to screen for Tra2 cofactors in Drosophila S2 cells is shown. Splicing of the M1 intron from pM-Luc transcripts leads to expression of firefly luciferase (Luc). The light gray exons and M1 intron derive from the endogenous Drosophila Tra2 gene. The initiation codon shown is naturally split by the intron and is in frame with luciferase coding sequences. The ISS element is indicated within M1 intron. Transcript from pftz-Luc contains exons and a constitutive intron from the Drosophila ftz gene. The same promoter and polyA signals are used in both constructs. (B) Luciferase activity from pM-Luc but not pftz-Luc is repressed in the presence of pT2 a plasmid expressing the Flag-tagged Tra2-PC isoform of Tra2 in cotransfection experiments. Results from luciferase assays (graph) and immunoblots probed with anti-Flag antibodies are shown. The position of Flag-Tra2 and two non-specific bands (nc) typically observed in such assays as well as molecular weight markers are indicated. (C) The effects of Tra2 on splicing of transcripts from both reporters, as detected by RT-PCR, is also shown. As expected, the ratio of amplification products from unspliced (U) to those of spliced (S) transcripts deriving from pM-Luc increases with higher levels of Tra2.
