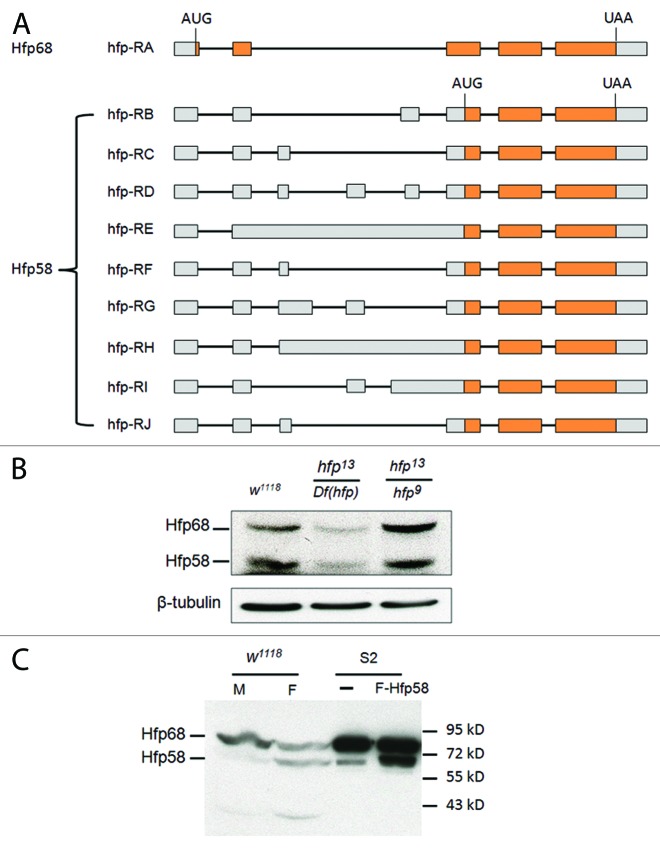
Figure 6. Hfp has two isoforms expressed in vivo. (A) The exon-intron patterns giving rise to various Hfp (Puf68) encoding mRNAs. The diagram was created based on the information in Gbrowse. Boxes correspond to exons, lines to introns. Gray shaded regions are predicted to be noncoding, orange box is predicted protein coding. Note that only the RA transcript has the potential to encode the Hfp68 isoform, all other transcripts are predicted to encode Hfp58. The initiation codons and stop condons are indicated. (B) A comparison of Hfp68 expression in lysates from a mixture of Drosophila male and female adult flies with various genotypes is shown. Both forms are observed in w1118 adults (carrying two wild type alleles of hfp), but are both reduced in hfp13/Df(hfp). Both hfp13 and hfp9 are partial loss-of-function mutations. (C) Expression of Hfp68 and Hfp58 in w1118 male (M) and female (F) adult flies is shown as detected by immunoblotting. For comparison, lysates from S2 cells (-) and S2 cells transfected with Flag-Hfp58 (F-Hfp58) were loaded on the same gel.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.