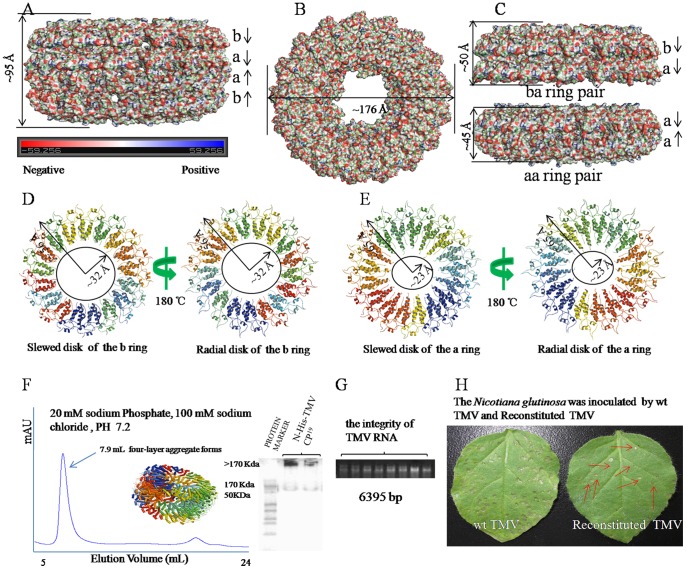
Figure 1. Crystal structure and function of the four-layer aggregate disk of N-His-TMV CP19.
(A) Electrostatic surface presentation of the N-His-TMV CP19 four-layer aggregate of ∼95 Å in height. The electrostatic surface was calculated in pyMOL. The complete four-layer aggregate is shown in four rings in the following order: b-ring, a-ring, a-ring, b-ring. (B) Electrostatic surface presentation of the N-His-TMV CP19 four-layer aggregate disk of ∼176 Å in diameter. (C) Electrostatic surface presentation of the ba-ring and aa-ring pairs. The aa-ring pair is sandwiched between the two b-rings. The a-ring and a-ring chains are anti-parallel and pack more tightly to ∼45 Å in height; the b-ring and a-ring chains are parallel and pack to ∼50 Å in height. (D) The slewed (radial) disk of the b-ring defines a 64 Å diameter axial pore based on residue Val 114 (bottom panel); (E) the slewed (radial) disk of the a-ring defines a 46 Å diameter axial pore based on residue Thr107 (bottom panel). (F) Assembly of the N-His-TMV CP19 four-layer aggregate, as measured by SEC and native-PAGE electrophoresis. (G) TMV RNA integrity was examined by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. (H) The N. glutinosa was inoculated with WT TMV and reconstituted TMV. The local lesions that were inoculated with reconstituted TMV are labeled with red arrows.