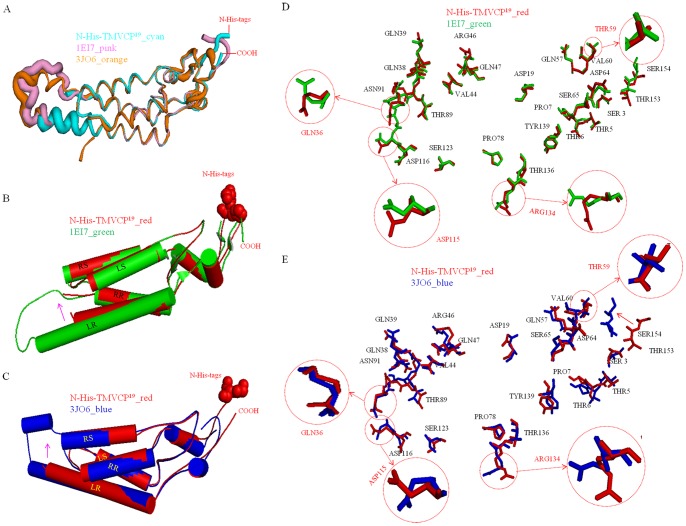
Figure 8. Structure comparisons between the previously reported TMV CP structure (PDB code 1EI7) and N-His-TMV CP19; and virus structure (PDB code 3JO6) and N-His-TMV CP19.
(A) The B factors of the atomic model are based on the atomic structure. Compared with TMV CP (PDB code 1EI7) and TMV CP (PDB code 3JO6), the N-His-TMV CP19 residues at the C-terminus loop (residues 148–154) have a low atomic B factor; the N-His-TMV CP19 in the low-radius inner loop [residues 104–111 of the a-ring (residues 107–111 of the b-ring)] have a high atomic B factor, indicating that the residues in these loops are disordered. In this structure, the disordered residues are stabilized by protein–protein hydrogen bonding interactions in the adjacent subunit. (B) Structure comparison between the TMV CP monomer (PDB code 1EI7) and the N-His-TMV CP19 monomer. The shifting N-His-TMV CP19 LR cylindrical helix is highlighted by an arrow. (C) Structure comparison between the TMV CP monomer (PDB code 3JO6) and the N-His-TMV CP19 monomer. The shifting N-His-TMV CP19 LR cylindrical helix is highlighted by an arrow. (D) Alignment of the side view of the TMV CP monomer (PDB code 1EI7) and the N-His-TMV CP19 monomer to show the different conformations in the main- and side-chain residues. The key residues in oligomer assembly are highlighted and labeled. (E) Alignment of the side view of the TMV CP monomer (PDB code 3JO6) and the N-His-TMV CP19 monomer to show the different conformations in the main- and side-chain residues. The key residues in oligomer assembly are highlighted and labeled.