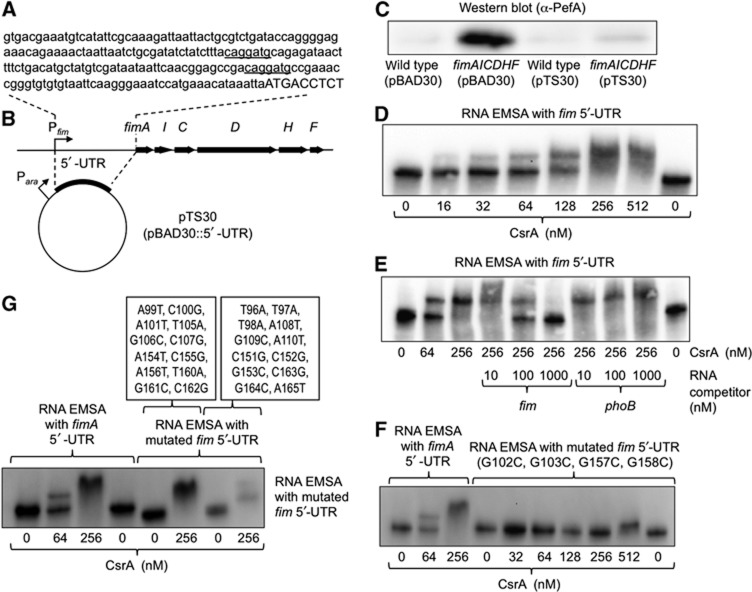
Figure 4.
The 5′-UTR of the fimA transcript suppresses PefA expression and binds to CsrA. (A) Sequence of the 5′-UTR of the fimA transcript according to Kroger et al (2012). Predicted CsrA-binding sites are underlined. Capital letters indicate the start of the pefA open reading frame. (B) Schematic depiction of the fimAICDHF operon and the cloning strategy for overexpressing the 5′-UTR of the fimA transcript. (C) Expression of PefA was detected in cell lysates of the indicated strains using western blot. Bacteria were grown for 48 h statically in the presence of 0.2% arabinose and carbenicillin. (D–G) Electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs). RNA protein complexes were separated on a native 5% TBE gel to perform EMSAs. 3′-end biotinylated fimA 5′-UTR RNA was incubated with the indicated concentrations of CsrA-6xHis dimers in the absence (D) or presence (E) of unlabelled competitor RNA. The concentrations of specific (fim) or non-specific (phoB) competitor RNA are indicated on the bottom of each lane. (F, G) 3′-end biotinylated fimA 5′-UTR RNA mutated at the indicated positions was incubated with the indicated concentrations of CsrA-6xHis dimers.
Source data for this figure is available on the online supplementary information page.