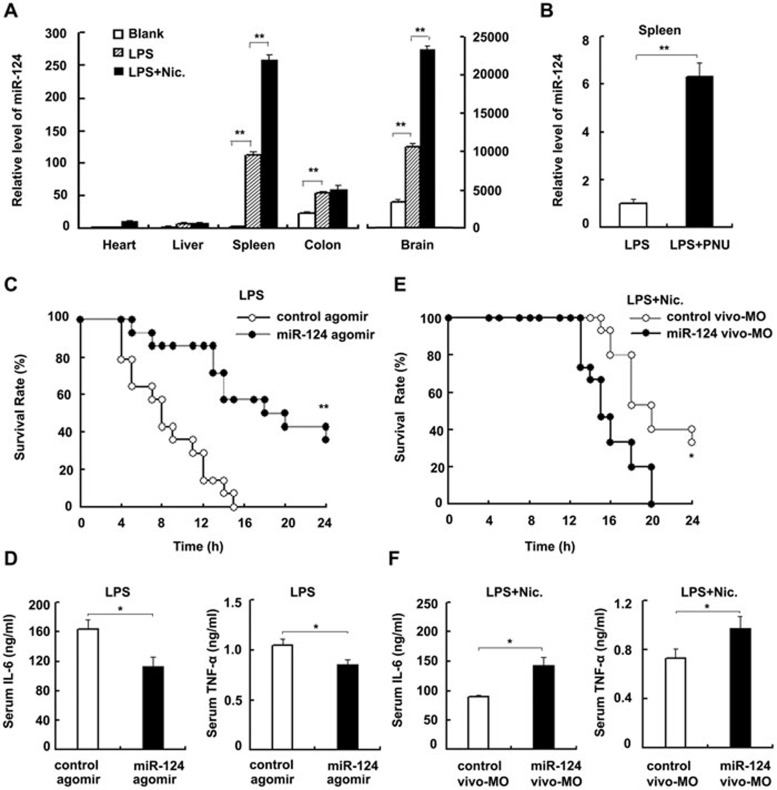
Figure 4.
miR-124 is essential for the anti-inflammatory effect of the cholinergic pathway in LPS-induced septic mice. (A) q-PCR of miR-124 in various tissues obtained from BALB/c mice injected intraperitoneally with 30 mg/kg LPS with or without 2 mg/kg nicotine for 3 h. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 6). (B) q-PCR of miR-124 in spleen obtained from BALB/c mice injected intraperitoneally with 30 mg/kg LPS in the presence or absence of 3 mg/kg PNU. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 6). (C) BALB/c mice were injected via the tail vein daily with 100 nmol/kg miR-124 agomir or matched control for 3 days. A lethal dose of LPS (30 mg/kg) was then administered. The survival rate was recorded every 2 h (n = 14). (D) ELISA detection of serum IL-6 and TNF-α obtained from BALB/c mice 6 h after treatment as described in C. Results are mean ± SD (n = 6). (E) BALB/c mice were injected via the tail vein daily with 12.5 mg/kg morpholino-conjugated miR-124 antisense (vivo-MO) or matched control for 3 days. They were then given intraperitoneally 30 mg/kg LPS together with 2 mg/kg nicotine. The survival rate was recorded every 2 h (n = 14). (F) ELISA detection of serum IL-6 and TNF-α obtained from BALB/c mice 6 h after treatment as described in E. Results are mean ± SD (n = 6). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 (Student's t-test in A, B, D and F, log-rank test in C and E).