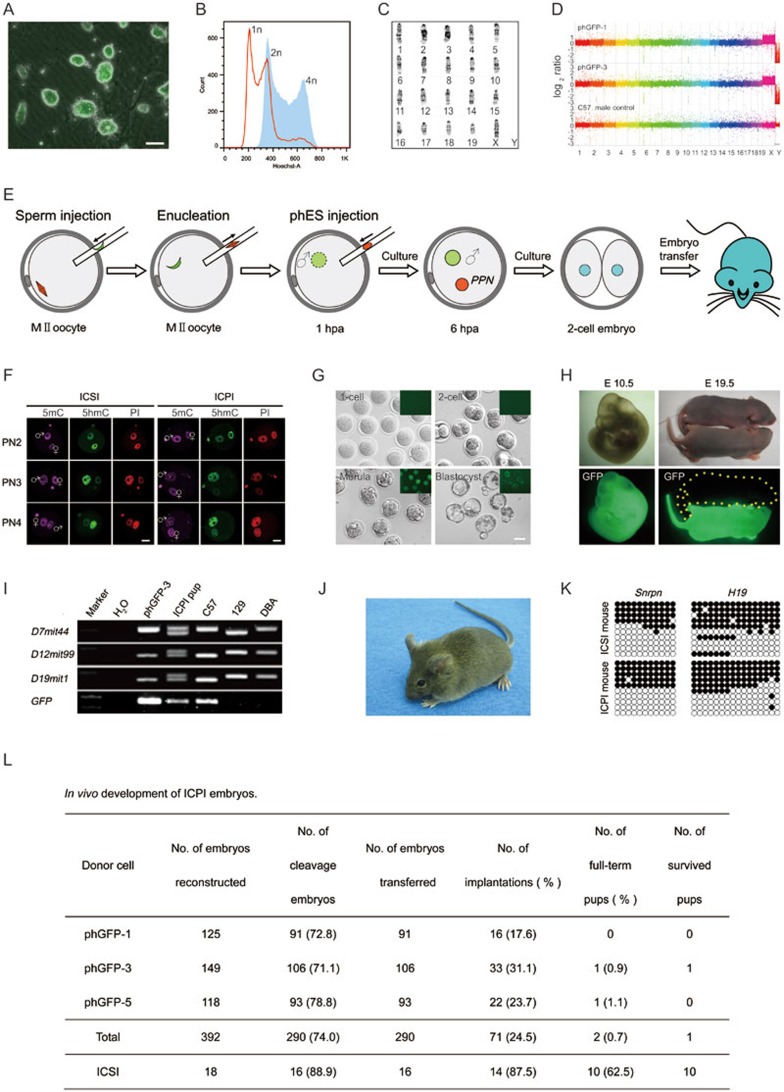
Figure 1.
Parthenogenetic haploid ES cells produce fertile mice. (A) Fluorescence detection of phES cells that carry an EGFP transgene. Scale bar, 50 μm. (B) DNA content of phES cells (phGFP-3, passage 11, red) analyzed by FACS. Cells were purified three times by FACS selection of G0/G1 phase haploid cells, followed by culturing for three more passages. Diploid ES cells (blue) with 2n chromosome sets were used as control. (C) Karyotype analysis of phES cell lines. Shown is the standard G-binding karyotype of phGFP-3 cells (passage 12) with 19 + X chromosomal set. (D) Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) analysis of two phES cell lines (phGFP-1 Passage 16, and phGFP-3 Passage 16). Comparative results of the genomic DNA of the phES cells and the control C57BL/6 male mouse kidney were shown as the y axis, on a log2 base scale. (E) Diagram showing the generation of phES pups. hpa, hours post activation. (F) 5mC and 5hmC staining of the reconstructed embryos (6-7 hpa) with pronucleus after sperm injection. The ICSI embryos were shown in the left panel, whereas reconstructed ICPI embryos were shown in the right panel. (G) Pre-implantation development of ICPI embryos produced by phES cell injection. Scale bar, 50 μm. (H) Left panel shows an E10.5 ICPI fetus with EGFP expression that was produced by phGFP-3. Right panel shows one P2 ICPI pup (phGFP-3) with EGFP expression, and one P2 wild-type ICSI pup. (I) Genetic background analysis of ICPI pup. Three simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) DNA markers from different chromosomes and the EGFP positive analysis showed that the pup was originated from hybrid genetic background, i.e., the C57BL/6 strain (phGFP-3 origin) and the 129Sv strain (sperm origin). Primer sequences were cited from the Mouse Genome Informatics website (http://www.informatics.jax.org/). (J) An adult male mouse produced by phES cell (phGFP-3) injection. (K) Bisulfite sequencing analysis of DMRs of imprinted genes Snrpn and H19. Mouse tail DNAs isolated from ICSI and phES adult off-springs were used. Filled circles represent methylated CpG sites, whereas open circles represent unmethylated CpG sites. Primer sequences were listed in Supplementary information, Table S3. (L) In vivo development of ICPI embryos.