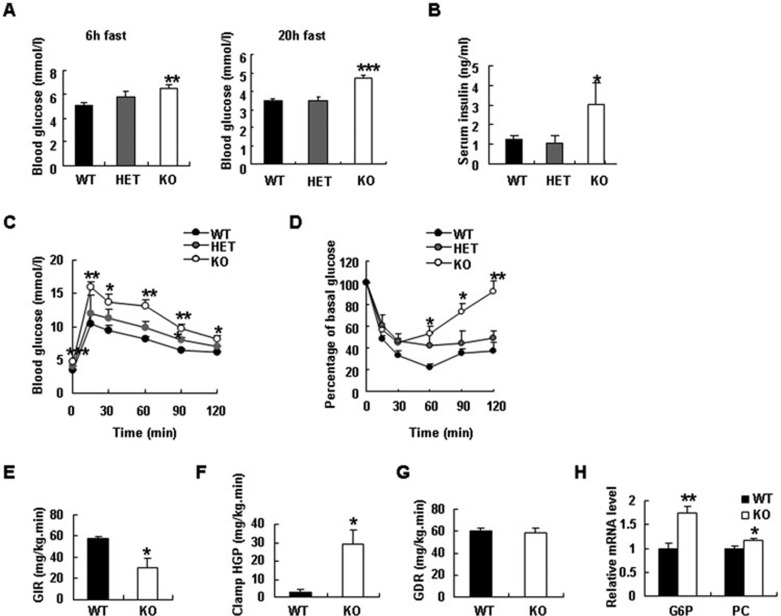
Figure 2.
IRTKS deficiency leads to insulin resistance. (A) Blood glucose levels in 3.5-month-old male IRTKS-KO, HET mice and WT littermates (n = 5). (B) Serum insulin levels in 3.5-month-old male IRTKS-KO, HET mice and WT littermates (n = 5-8). (C) Glucose tolerance test (GTT) in IRTKS-KO, HET mice and WT littermates (n = 5-8) (fasted overnight and then ip glucose (1.5 g/kg)). (D) Insulin tolerance test (ITT) (ip insulin (1 U/kg)) (n = 5-8). (E-G) In hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp studies, glucose infusion rate (GIR) (E), clamped hepatic glucose production (HGP) (F) and glucose disappearance rate (GDR) (G) were evaluated in 5-month-old male IRTKS-KO mice and WT littermates (n = 4). (H) Relative mRNA levels of glucose-6-phosphatase (G6P) and pyruvate carboxylase (PC) in IRTKS-KO mice and WT littermates (n = 4). Data are presented as mean ± sem. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus control.