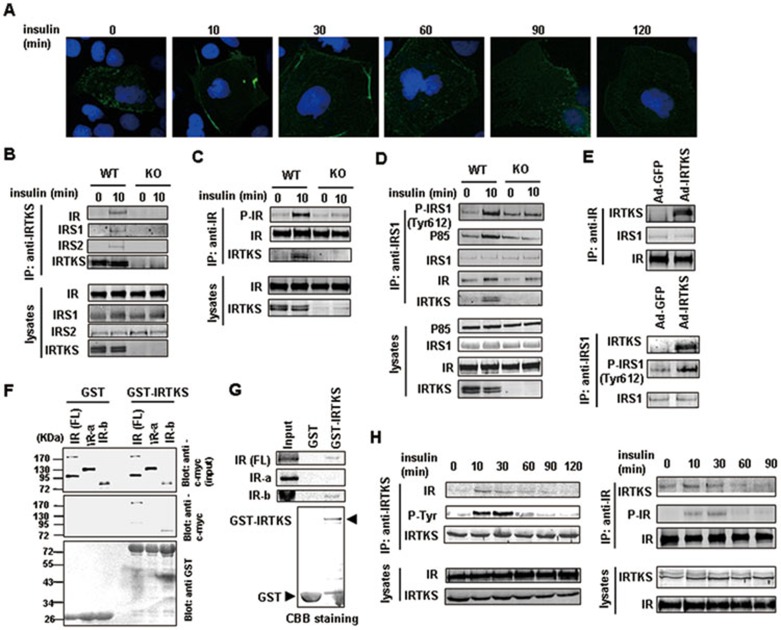
Figure 5.
IRTKS binds to insulin receptor and IRS1. (A) Dynamic images of Huh-7 cells transfected with the recombinant expression plasmid containing GFP-tagged IRTKS were shown upon insulin stimulation for the indicated times. (B-D) Co-IP experiments in liver extracts of IRTKS-KO mice and WT littermates with anti-IRTKS, -IR and -IRS1 antibodies, respectively. (E) Co-IP experiments in liver extracts of IRTKS-KO mice infected with Ad-GFP or Ad-IRTKS were performed using anti-IR and -IRS1 antibodies, respectively. (F, G) GST pull-down assays. (F) Glutathione-Sepharose beads coupled with either GST alone or GST-IRTKS were incubated with YY-8103 cell lysates containing myc-tagged full-length (FL) IR, myc-IRα or myc-IRβ subunits. The positions of the molecular mass markers were shown on the left. (G) In vitro translated 35S-labeled IR (FL), IRα and IRβ subunits were incubated with purified GST or GST-IRTKS fusion protein coupled with Glutathione-Sepharose beads, respectively. The bound proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by autoradiography. Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) staining on SDS-PAGE showed the GST and GST-IRTKS proteins. (H) Co-IP experiments with anti-IRTKS or -IR antibodies were performed in liver extracts of C57BL/6 mice injected with insulin (1 U/kg) for the indicated times. Western blotting assay was employed to assess the dynamic change of association of IRTKS with IR.