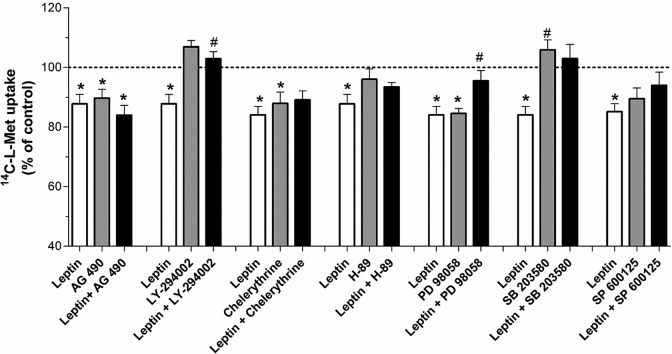
Figure 8.
Effect of the inhibitors of intracellular signaling pathways upon hyperleptinemia-induced inhibition of 14C-l-methionine (14C-l-Met) uptake by Bewo cells. Initial rates of uptake were determined in cells incubated for 6 minutes with 14C-l-Met 250 nmol/L, after treatment for 48 hours with leptin 100 ng/mL (leptin), AG 490 5 µmol/L (AG 490), leptin 100 ng/mL + AG 490 5 µmol/L (leptin + AG 490), LY-294002 1 µmol/L (LY-294002), leptin 100 ng/mL + LY-294002 1 µmol/L (leptin + LY-294002), chelerythrine 0.1 µmol/L (chelerythrine), leptin 100 ng/mL + chelerythrine 0.1 µmol/L (leptin + chelerythrine), H-89 1 µmol/L (H-89), leptin 100 ng/mL + H-89 1 µmol/L (leptin + H-89), PD 98058 2.5 µmol/L (PD 98058), leptin 100 ng/mL + PD 98058 2.5 µmol/L (leptin + PD 98058), SB 203580 9.6 µmol/L (SB 203580), leptin 100 ng/mL + SB 203580 9.6 µmol/L (leptin + SB 203580), SP 600125 5 µmol/L (SP 600125), and leptin 100 ng/mL + SP 600125 5 µmol/L (leptin + SP 600125; n = 9-13). Shown is arithmetic mean ± standard error of the mean. *Significantly different from the respective control (P < .05) and #significantly different from leptin (100 ng/mL; P < .05).