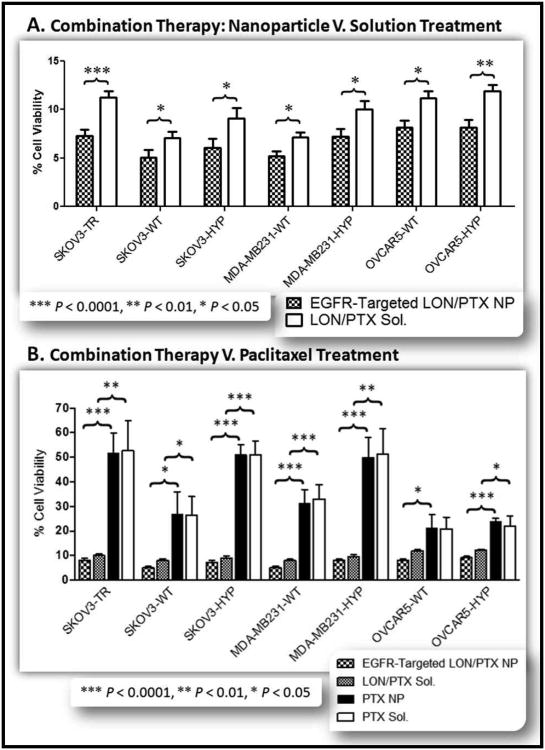
Figure 11. Lonidamine and Paclitaxel Combination Therapy.
A panel of seven cell lines was used to evaluate the efficacy of combination lonidamine/paclitaxel therapy. The cell lines included SKOV3TR cells, SKOV3 wild type cells (WT), SKOV3 hypoxic cells (HYP), MDA-MB-231 wild type cells, MDA-MB-231 hypoxic cells, OVCAR5 wild type cells, and OVCAR5 hypoxic cells. (A). Each cell line was treated with EGFR-Targeted lonidamine/paclitaxel loaded nanoparticles (EGFR-Targeted LON/PTX NP; black and white checkered bar) and with lonidamine/paclitaxel solution (LON/PTX Sol; solid white bar). All treatment doses were 10 μM lonidamine and 1 μM paclitaxel. Combination therapy dramatically reduced the cell viability for all cell lines to below 10% cell viability for all cell lines treated with the combination nanoparticles and to approximately 5% cell viability for the wild type SKOV3 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Each treatment represents an n=7. (B.) Combination paclitaxel/lonidamine treatment with 10 μM lonidamine and 1 μM paclitaxel was compared to treatment with 1 μM paclitaxel alone (in nanoparticle and solution forms). The panel of cells were treated with EGFR-Targeted lonidamine/paclitaxel loaded nanoparticles (EGFR-Targeted LON/PTX NP; black and white checkered bar), lonidamine/paclitaxel solution (LON/PTX Sol; gray checkered bar), paclitaxel nanoparticles (PTX NP; solid black bar), and with paclitaxel solution (PTX Sol; solid white bar). As illustrated, 1 μM paclitaxel is the approximate IC50 for the MDR SKOV3TR cells and for the hypoxic SKOV3 cells and the hypoxic MDA-MB-231 cells. This is reduced by 40% when combined with lonidamine treatment. Each treatment represents an n=7.