Fig. 1.
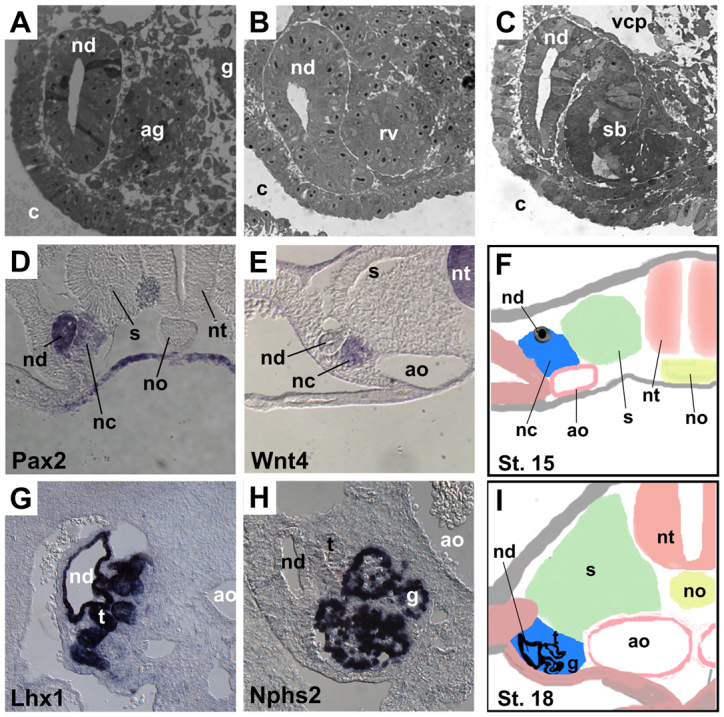
Development of the chick mesonephros. (A-C) Plastic sections from a single stage 18 embryo, from posterior (A) to anterior (C) axial levels, illustrating stages in the differentiation of mesonephric nephrons, including pretubular aggregate (ag), renal vesicle (rv) and S-shaped body (sb). (D,E) In situ hybridization at stage 16 for Pax2 (D) and Wnt4 (E), showing Pax2 expression in nephric duct and nephrogenic cord (D) and Wnt4 expression in the condensing pretubular aggregate (E). (G,H) In situ hybridization at stage 25 for Lhx1 (G) and Nphs2 (H) showing Lhx1 expression in the nephric duct and tubules (G) and Nphs2 expression in the podocytes of the glomerulus (H). (F,I) Diagrams of sections through the mesonephric regions of stage 15 and 18 embryos for orientation purposes. Note that in F, the undifferentiated nephrogenic cord is located between the nephric duct and the aorta. In I, the embryo has begun to fold, resulting in the nephric duct being located laterally, but the relationships between the nephric duct, the IM and the aorta are preserved. Within the differentiating IM in I, the tubules are located laterally, closer to the duct, and the glomeruli are located medially, closer to the aorta. ag, pretubular aggregate; ao, aorta; c, coelom; g, glomerulus; nc, nephrogenic cord; nd, nephric duct; no, notochord; nt, neural tube; rv, renal vesicle; s, somite; sb, s-shaped body; t, tubule; vcp, posterior cardinal vein.
