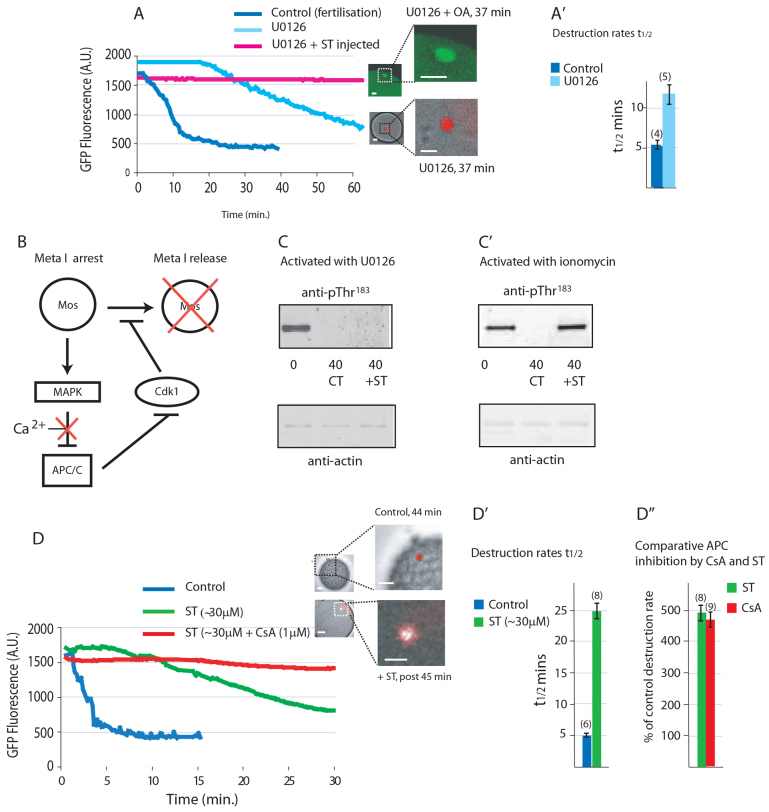
Fig. 4.
Inhibition of PP2A with ST protein prevents activation both by U1026 and calcium. (A) U0126 triggers Cyclin B Y170A destruction, whereas injection of ST protein prevents U0126-mediated destruction of Cyclin B Y170A (n=7 from three animals). The spindle (green) remains intact 37 minutes after addition of U0126 (20 μM), at which time control eggs had exited meiosis with DNA decondensed (red) within a pronucleus. (A′) Cyclin B Y170A destruction rate, expressed as mean of t1/2 values ±s.e.m., in U0126-treated eggs is approximately half that of control fertilised eggs (n in parentheses). (B) Schematic of our hypothesis for metaphase I (Meta I) arrest and how it is broken by a calcium signal. (C) Injection with ST protein fails to prevent dephosphorylation of T183 in U0126-activated eggs after 40 minutes (n=3). (C′) T183 remains phosphorylated after 40 minutes in eggs injected with ST and activated with ionomycin (n=3). (D) Cyclin B Y170A destruction is impaired (n=10 from three animals). DNA decondensation (red) and polar body emission inhibited in eggs injected with ST protein and activated with ionomycin (n=8 from three animals), whereas destruction is blocked in eggs injected with ST protein and treated with CsA prior to activation with ionomycin. (D′) Cyclin B Y170A destruction rate, expressed as mean t1/2 values ±s.e.m., is five times slower in ST-injected eggs (n in parentheses). (D′) Comparison of APC/C inhibition by ST protein and CsA showing a similar level of inhibition. Error bars represent s.e.m. All graphs shown are example traces. Scale bars: in A and D, 20 μm in whole egg images, 10 μm in enlarged images.