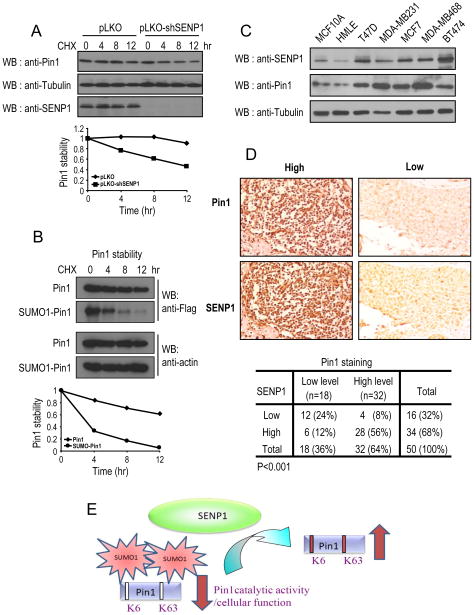
Figure 7.
SENP1 levels positively correlate with Pin1 levels in human breast cancer tissues.
A, B, MCF10 Ras/Neu cells expressing control and SENP1 shRNA or MCF10 Ras/Neu cells expressing Pin1shRNA and SENP1 shRNA were transfected with Flag-Pin1, or Flag-SUMO-Pin1 were treated with cycloheximide (100 μg/ml) for indicated times, followed by immunoblotting. C, The same amounts of total lysates prepared from spontaneously immortalized normal human mammary epithelial cell lines and human breast carcinoma-derived cell lines were subjected to immunoblotting. D, Serial sections of tissue arrays of 50 breast cancer tissue specimen were subjected to immunohistochemistry using anti-Pin1 antibodies (upper panel) or anti-SENP1 antibodies (low panel), and visualized by the DAB staining (B). In each sample, SENP1 expression and Pin1 levels were semi-quantified in a double-blind manner as high or low according to the standards presented in (B) and summarized in (C) Their correlation was analyzed by Spearman rank correlation test (P<0.001). E, A scheme depicts that SENP1 binds and deSUMOylates Pin1 and promotes its Pin1 activity and function.