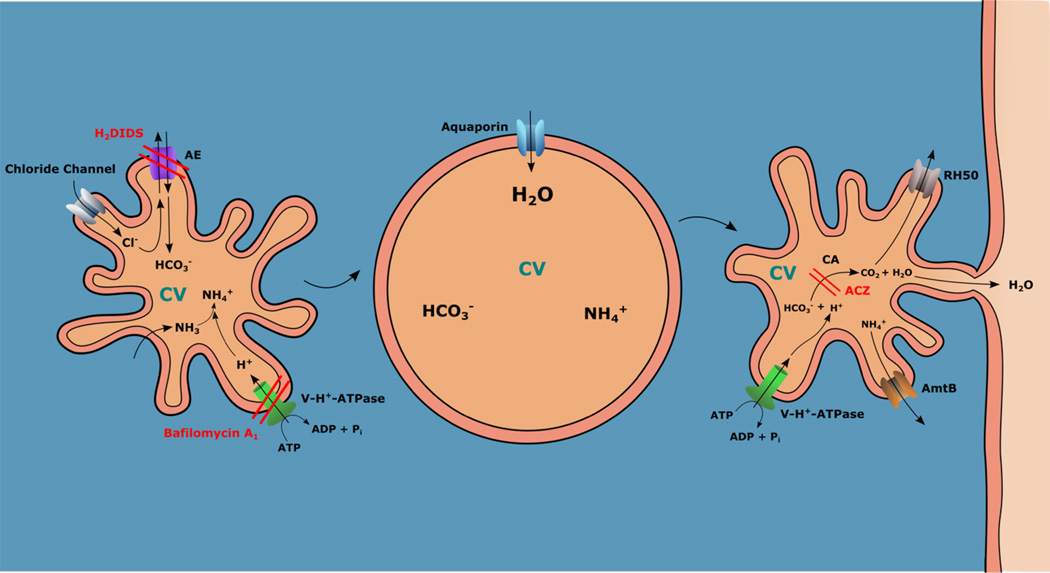
Figure 3. Model proposed for filling of the CVC in protists.
Ammonia (NH3) is transported to the CVC where it combines with H+ pumped in by the action of the vacuolar H+-ATPase (which is inhibited by bafilomycin A1) to generate ammonium (NH4+), which is charged and retained. An anion exchanger (AE, which is inhibited by H2DIDS) transports HCO3− in exchange of Cl−, which enters the vacuole through a chloride channel. NH4+ and HCO3− are osmolytes that attract water, which enters through an aquaporin (AQP) and swells the CV. The CV contacts the plasma membrane (kiss and run) through a porosome, releasing water to the medium. A carbonic anhydrase (which is inhibited by acetazolamide, ACZ) generates CO2 from HCO3− and H+ (pumped in by the V-H+-ATPase). CO2 is released into the cytosol through the protein RH50, while ammonium is released into the cytosol through an ammonium transporter (AmtB).