Figure 6. Which attractor dominates when the majority effect and the expert effect apply simultaneously?
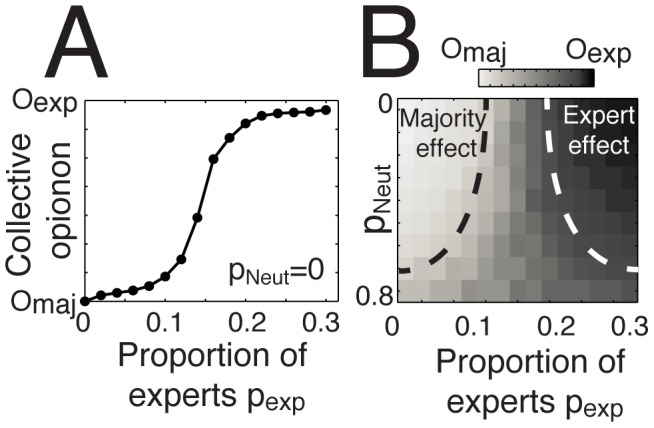
(A) The evolution of collective opinion when varying the relative proportion of experts pExp , holding an opinion Oexp and a high confidence level Cexp = 6, and the proportion of people in the majority group pmaj holding an opinion Omaj and a low confidence level randomly chosen in the interval Cmaj = [1 3]. Here, the number of neutral individuals is fixed to pNeut = 0. (B) Phase diagram showing the parameter space where the majority or the expert effects applies, when increasing the proportion of neutral individuals pNeut holding a random opinion and a low confidence level randomly chosen in the interval Cuni = [1 3]. The schematic regions delimited by black or white dashed lines show the zones where the collective opinion converges toward the majority or the expert opinion, respectively. In the transition zone, the collective opinion converges somewhere between Oexp and Omaj. In some rare cases, the crowd splits into two groups or more.
