Figure 2.
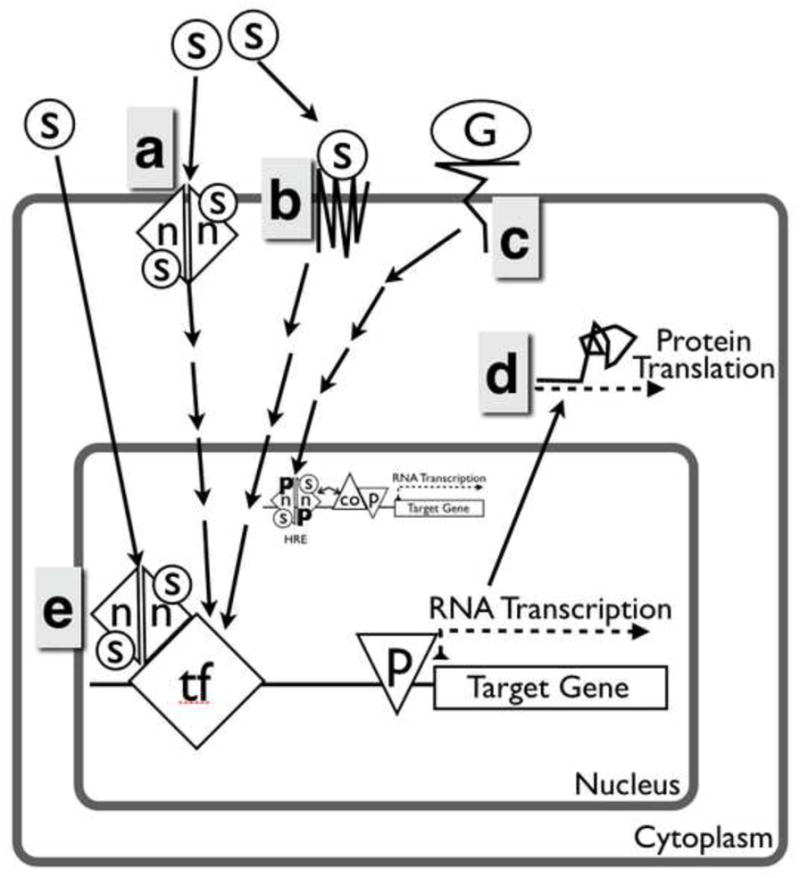
Non-classical actions of nuclear oestrogen and progesterone receptors. (a) Membrane-associated steroid receptors, either isoforms of classical receptors, or (b) unrelated transmembrane receptors recognize steroid hormones and initiate a cytoplasmic signalling cascade. (c) Growth factors signalling can act by causing post-translational modifications of nuclear steroid receptors. (d) Additionally, oestrogen and progesterone can modulate expression by altering mRNA turnover and translation. (e) Alternatively, steroids can bind classical nuclear receptors, which act by binding other proteins rather than DNA. co = co-regulator; G = growth factor; HRE = hormone response element; n = nuclear steroid receptor monomer; ns = non-steroid; p = RNA polymerase; s = steroid; TF = transcription factor.
