Figure 1.
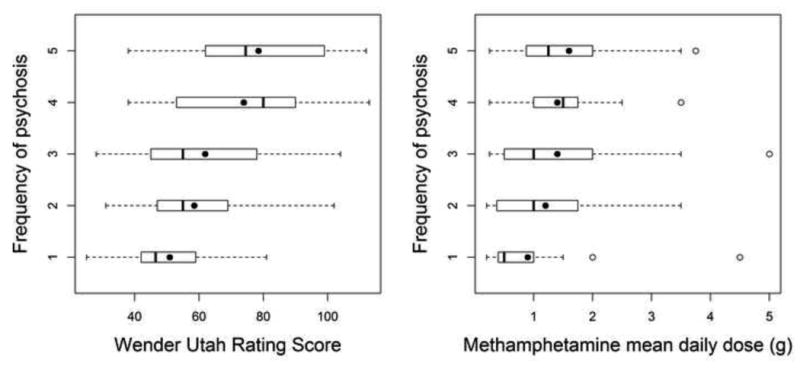
Association between Wender Utah Rating Scale of childhood attention and methamphetamine daily dose with frequency of psychosis measured on a Likert scale. Box plots define the values for median, range, 25th and 75th percentiles. Means are represented by filled circles. The proportional odds model was used to calculate the odds (OR) of developing more frequent psychosis for higher Wender Utah scores (OR = 1.04, p < 0.0001) and larger methamphetamine daily dose (OR = 1.61, p = 0.003), respectively.
