Figure 5. Differential filtering of somatic and dendritic input persists for a variety of cell morphologies and a gradual distribution of the active current.
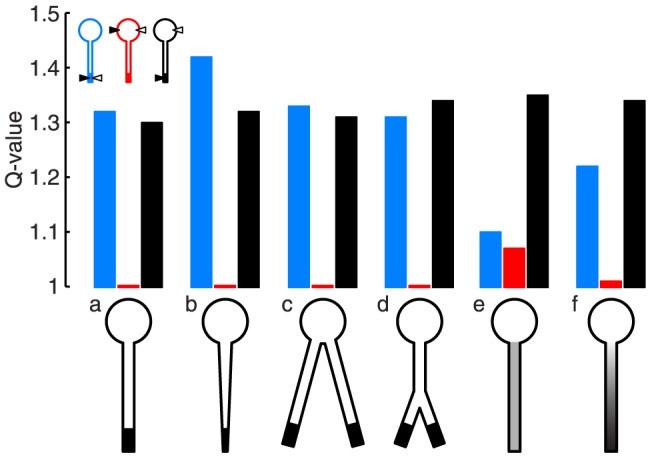
Q-values of the dendritic input impedance (blue), somatic input impedance (red), and dendro-somatic transfer impedance (black). a: The default model from Figures 1B, 2C, 3, and 4 (length of passive cable 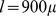 m, length of active distal end
m, length of active distal end 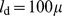 m, dendrite diameter
m, dendrite diameter 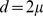 m, peak conductance in active segment
m, peak conductance in active segment 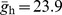 nS). b: Tapering of diameter towards the dendritic end (dendrite diameter gradually decreases from
nS). b: Tapering of diameter towards the dendritic end (dendrite diameter gradually decreases from 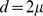 m to
m to 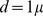 m). c: Neuron with two dendrites, both with the same parameters as model a. d: Branching neuron (length of primary dendrite
m). c: Neuron with two dendrites, both with the same parameters as model a. d: Branching neuron (length of primary dendrite 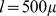 m, length of passive parts of both daughter dendrites
m, length of passive parts of both daughter dendrites 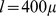 m, length of active dendritic ends
m, length of active dendritic ends 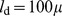 m). e: Uniform distribution of h-conductances (peak conductance density
m). e: Uniform distribution of h-conductances (peak conductance density 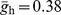 mS/cm
mS/cm ). f: Exponential distribution of h-conductances (
). f: Exponential distribution of h-conductances (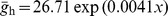
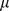 S/cm
S/cm ). Note that the total h-conductance and the length of the path between distal dendritic end and the soma were the same in all considered cases.
). Note that the total h-conductance and the length of the path between distal dendritic end and the soma were the same in all considered cases.
