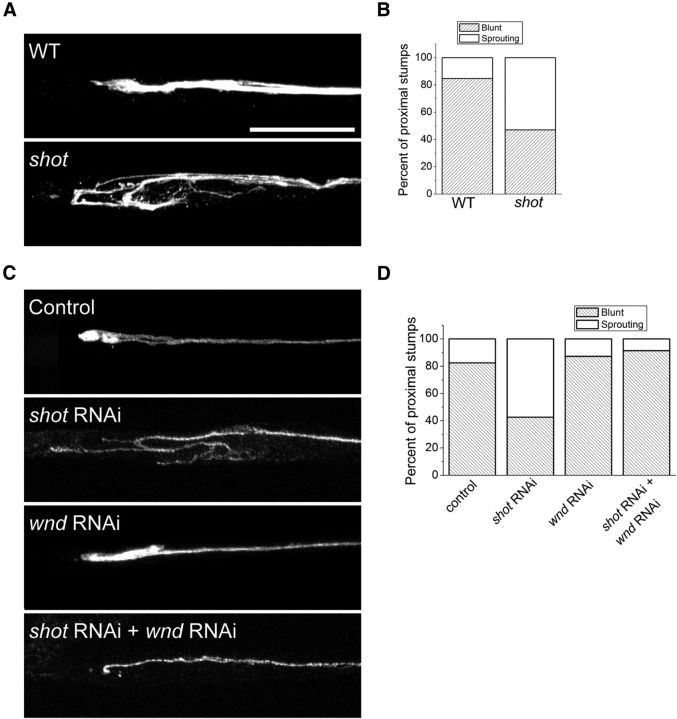
Figure 7.
shot mutants have enhanced axonal sprouting after injury. Axons are labeled by driving expression of UAS-mCD8-GFP by m12-Gal4. Axons from (A) WT animals do not yet form extensive new branches by 7 h after injury, whereas in shotvv/shot3 (shot) mutants a large growth cone with multiple sprouting sites can be seen more frequently than in WT (p < 0.001, χ2 test, n > 30 axons for each genotype). The number of blunt versus sprouting axonal stumps was counted, and their frequencies are presented in B. C, Same analysis was done on UAS-dcr2;; UAS-mCD8-GFP, m12-Gal4/+ (control), UAS-dcr2; UAS-mCD8-GFP, m12-Gal4/UAS-shot-RNAi; (shot RNAi), UAS-dcr2; UAS-wnd-RNAi/+;UAS-mCD8-GFP, m12-Gal4/+ (wnd RNAi), and UAS-dcr2; UAS-wnd-RNAi /UAS-mCD8-GFP,m12-Gal4; UAS-shot-RNAi/+ (shot RNAi; wnd RNAi) and quantified in D. n > 50 axons for each genotype. Scale bar, 25 μm.