Figure 3.
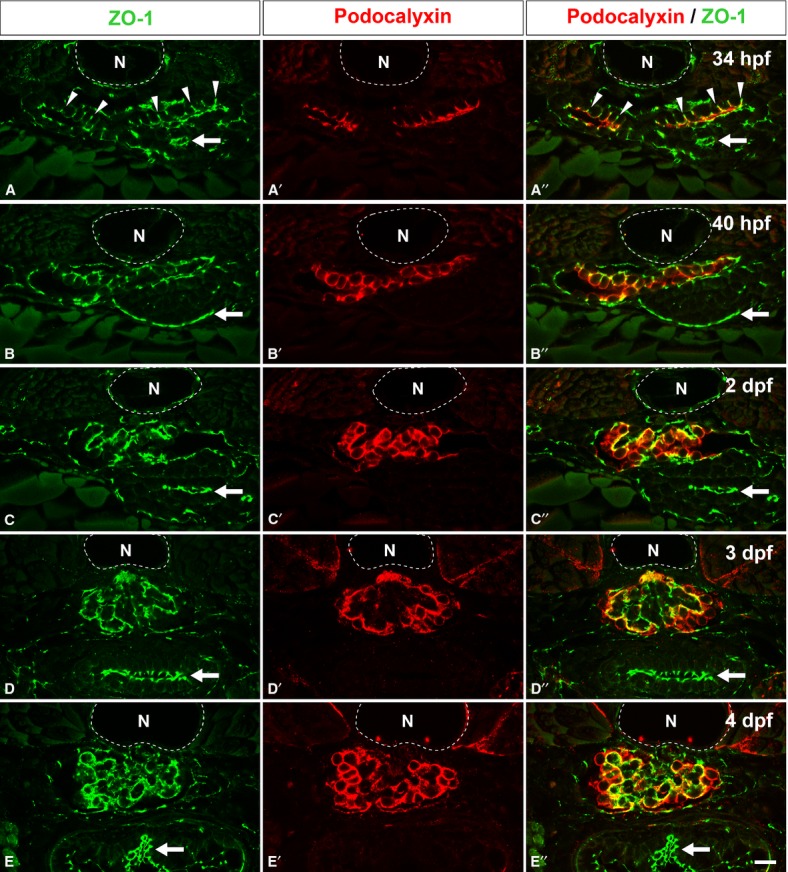
Localization of Podocalyxin in the developing pronephric glomerulus. Double immunofluorescence labeling for ZO-1 (green) and Podocalyxin (red) was performed to examine the localization of Podocalyxin in zebrafish at 34 hpf (A-A′′), 40 hpf (B-B′′), 2 dpf (C-C′′), 3 dpf (D-D′′), and 4 dpf (E-E′′). At 34 hpf, immunoreactivity for ZO-1 is found at the tight junctions between the primitive columnar podocytes (arrowheads in A, A′′). In addition, Podocalyxin is localized at the apical membrane, which is recognized as the luminal surface membrane above the tight junctions (A′, A′′). At 40 hpf, the Podocalyxin-localized apical membrane is expanded (B-B′′). After 2 dpf, immunoreactivity for ZO-1 is found along the glomerular wall (C, D, and E), which indicates that interdigitation between the podocytes has become extensively. The Podocalyxin signal is found along the entire surface of the podocyte cell bodies (C′-E′, C′′-E′′). (A′′-E′′) show the merged images. N, notochord; arrows, tight junctions in the intestinal epithelium. Bar scale, 10 μm.
